Prevalence of Long COVID Syndrome and its Association With Blood Group: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38468999
- PMCID: PMC10926967
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53966
Prevalence of Long COVID Syndrome and its Association With Blood Group: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic rapidly spread across the globe since 2020. It was characterized by a number of acute signs and symptoms. There were, however, some new-onset signs and symptoms labelled as "Long COVID". This study was conducted to study its prevalence and associations with blood group.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted in Islamabad for patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2020-2021. Information was collected through an online and physical questionnaire regarding personal demographics, symptoms during and after COVID-19, and blood group. The data was analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0 (Released 2017; IBM Corp., Armonk, New York, United States).
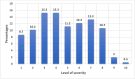
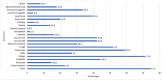
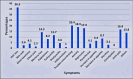
Results: The study identified 196 participants out of which 48.5% were male and 51% were female, with a median age of 30. Most participants (62.2%) belonged to the Punjabi ethnicity. The mean BMI was 25.56 kg/m2. The majority of the study participants reported having blood group B (n=76) followed by A (n=52). Acute symptoms were experienced by 95.4% of participants, with fatigue being the most persistent symptom at four weeks (45.9%). After four weeks, 63.3% of participants reported new symptoms like hair loss. Females were found more likely to experience long COVID symptoms. The perceived severity of acute infection was significantly associated with long COVID symptoms (p=<0.01). There was no association found between long COVID and blood group (p=0.158).
Conclusion: There was no association found between long COVID and ABO blood groups. Females were more likely than males to experience long COVID. Long COVID was found to be more likely to develop in those with perceived severe acute infection, highlighting the need for further research regarding aggressive care from the onset of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: abo blood groups; blood group; coronavirus disease 2019; covid-19; cross sectional studies; fatigue; long covid; prevalence.
Copyright © 2024, Butt et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation of Age, Gender, ABO Blood Group and Rh Factor in COVID-19 Infection: A Cross-Sectional Study in Udaipur, Rajasthan, India.Cureus. 2024 Apr 8;16(4):e57798. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57798. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38721205 Free PMC article.
-
Post-COVID-19 Illness Trend in a Local Community in Bangladesh.Cureus. 2023 Sep 26;15(9):e45998. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45998. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37900461 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Adverse Effects of Vaccines Against SARS-COV-2.Cureus. 2022 Jul 27;14(7):e27379. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27379. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36046318 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Seeking Behaviour and Its Determinants Following the COVID-19 Pandemic.Cureus. 2024 Jan 13;16(1):e52225. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52225. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38347970 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Symptoms of COVID-19: One-Year Follow-Up Study.Cureus. 2022 Jun 14;14(6):e25937. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25937. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35844318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. [ Apr; 2021 ]. 2020. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera... https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera...
-
- Worldometer: COVID-19 coronavirus disease. [ Jun; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Symptoms of COVID-19. [ Apr; 2021 ]. 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
-
- Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31986264/ Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Covid-19: what do we know about "long covid"? Mahase E. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32665317 BMJ. 2020;370:0. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources