Circulating IL-6 and not its circulating signaling components sIL-6R and sgp130 demonstrate clinical significance in NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 38469154
- PMCID: PMC10926441
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1324898
Circulating IL-6 and not its circulating signaling components sIL-6R and sgp130 demonstrate clinical significance in NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
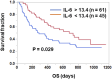
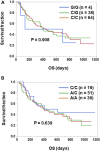
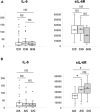
Introduction: Clinical roles of plasma IL-6 levels have been reported in patients with various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). However, the roles of other IL-6 signaling components, soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) and soluble gp130 (sgp130), in the plasma have not been elucidated. Methods: Blood was collected from 106 patients with NSCLC before initiation of ICI treatment (anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibody). Plasma levels of IL-6, sIL-6R, sgp130, and their complexes were assessed by Cox regression hazard model to evaluate their clinical significance. The clinical role of IL-6 or IL-6R genetic polymorphisms was also analyzed. Results: Cox regression analysis showed that higher plasma IL-6 levels significantly predicted unfavorable overall survival (OS; hazard ratio [HR] 1.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.05-1.68, p = 0.012) in NSCLC patients treated with ICIs. However, plasma sIL-6R and sgp130 levels showed no prognostic significance (p = 0.882 and p = 0.934, respectively). In addition, the estimated concentrations of binary IL-6:sIL-6R and ternary IL-6:sIL-6R:sgp130 complexes and their ratios (binary/ternary complex) were not significantly associated with OS (p = 0.647, p = 0.727, and p = 0.273, respectively). Furthermore, the genetic polymorphisms of IL-6 (-634G>C) and IL-6R (48892A>C) showed no clinical role by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (p = 0.908 and p = 0.639, respectively). Discussion: These findings demonstrated the clinical significance of plasma levels of IL-6, but not of other IL-6 signaling components, sIL-6R and sgp130, suggesting that classical IL-6 signaling, but not trans-signaling, may be related to anti-tumor immune responses in cancer patients treated with ICIs.
Keywords: IL-6; PD-1; PD-L1; immune checkpoint inhibitor; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R); soluble glycoprotein 130 (sgp130).
Copyright © 2024 Nakahara, Kouro, Motoyama, Miura, Fujita, Igarashi, Higashijima, Matsuo, Himuro, Wei, Horaguchi, Tsuji, Mano, Komahashi, Saito, Azuma and Sasada.
Conflict of interest statement
YN has received honoraria from Ono, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, and Bristol Myers Squibb, and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb. SM has received honoraria from Ono. HS has received honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, and Ono, and research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, and Ono. KA has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono, and Chugai. TS has received honoraria from Chugai and Bristol Myers Squibb, and research funding from Taiho and BrightPath Biotherapeutics. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6·soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 4;293(18):6762-6775. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001163. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29559558 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of IL-6 Signalling Components as Predictors of Severity and Outcome in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 May 13;13:891456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.891456. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634332 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of humanized anti-IL-6R antibody, tocilizumab on the activity of soluble gp130, natural inhibitor of IL-6 signaling.Rheumatol Int. 2009 Feb;29(4):397-401. doi: 10.1007/s00296-008-0703-8. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Rheumatol Int. 2009. PMID: 18802703
-
The role of interleukin-6 and of its soluble receptors in the biocompatibility of dialysis treatment.Semin Nephrol. 2004 Sep;24(5):492-4. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2004.06.001. Semin Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15490418 Review.
-
Interleukin-6 and its receptors: a highly regulated and dynamic system.Cytokine. 2014 Nov;70(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.05.024. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24986424 Review.
Cited by
-
Tocilizumab improves the efficacy of anti-PD-1 in a patient with advanced gastroesophageal junction cancer: a case report.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 4;15:1530387. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1530387. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40255422 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific cytokine signatures as predictors of anti-PD1 therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1583421. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1583421. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40589738 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cytokine Gene Polymorphisms in Rehabilitation Outcome After Traumatic Brain Injury.Cells. 2025 Jul 10;14(14):1056. doi: 10.3390/cells14141056. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demichele A., Gray R., Horn M., Chen J., Aplenc R., Vaughan W. P., et al. (2009). Host genetic variants in the interleukin-6 promoter predict poor outcome in patients with estrogen receptor-positive, node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 69, 4184–4191. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2989 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaillard J., Pugniere M., Tresca J., Mani J., Klein B., Brochier J. (1999). Interleukin-6 receptor signaling. II. Bio-availability of interleukin-6 in serum. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 10, 337–344. - PubMed
-
- Garbers C., Thaiss W., Jones G. W., Waetzig G. H., Lorenzen I., Guilhot F., et al. (2011). Inhibition of classic signaling is a novel function of soluble glycoprotein 130 (sgp130), which is controlled by the ratio of interleukin 6 and soluble interleukin 6 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 42959–42970. 10.1074/jbc.M111.295758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

