Urtica pilulifera leaves extract mitigates cadmium induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of antioxidants, inflammatory markers and Nrf-2 signaling in mice
- PMID: 38469182
- PMCID: PMC10925629
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1365440
Urtica pilulifera leaves extract mitigates cadmium induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of antioxidants, inflammatory markers and Nrf-2 signaling in mice
Abstract
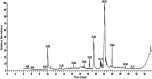
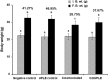
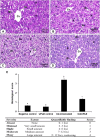
Introduction: Cadmium (Cd) is a harmful heavy metal that results in many toxic issues. Urtica pilulifera showed potential pharmaceutical applications. This study investigated the possible ameliorative mechanism of Urtica pilulifera leaves extract (UPLE) against hepatotoxicity induced by cadmium chloride (CdCl2) in mice. Methods: In vitro phytochemical screening and the metal-chelating activity of UPLE were ascertained. Four groups of forty male mice were used (n = 10) as follows; Group 1 (G1) was a negative control. G2 was injected i.p., with UPLE (100 mg/kg b. wt) daily. G3 was injected i.p., with Cd (5 mg/kg b. wt) daily. G4 was injected with Cd as in G3 and with UPLE as in G2. On day 11, the body weight changes were evaluated, blood, and serum samples were collected for hematological and biochemical assessments. Liver tissues were used for biochemical, molecular, and histopathological investigations. Results: The results showed that UPLE contains promising secondary metabolites that considerably lessen the negative effects of Cd on liver. Furthermore, UPLE inhibited oxidative stress and inflammation; restored antioxidant molecules; and promoted nuclear-related factor-2 (Nrf-2) expression. Also, UPLE improved the histopathological alterations induced by Cd. Discussion: This study explored the beneficial role of UPLE treatment in Cd-induced liver injury through enhancing Nrf-2 signaling and antioxidant enzyme gene expression in the liver of mice. Therefore, UPLE could have valuable implications against hepatotoxicity induced by environmental cadmium exposure. Which can be used as a chelating agent against Cd.
Keywords: Urtica pilulifera; antioxidants; cadmium; hepatotoxicity; nuclear-related factor-2.
Copyright © 2024 Hussein, Ben Bacha, Alonazi, Alwaili, Mobasher, Alburae, Banjabi and El-Said.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective effect of eugenol on hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress induced by cadmium in male rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111588. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111588. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33862491
-
Musa sp. Leaves Extract Ameliorates the Hepato-Renal Toxicities Induced by Cadmium in Mice.Molecules. 2022 Jan 16;27(2):559. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020559. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056874 Free PMC article.
-
The potential hepatoprotective effect of royal jelly against cadmium chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is mediated by suppression of oxidative stress and upregulation of Nrf2 expression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:1490-1498. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.089. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30119224
-
Sinapic Acid Ameliorates Cadmium-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 28;13(5):1065. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051065. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426893 Free PMC article.
-
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injuries Through Nutraceuticals via Amelioration of Nrf-2 Signaling.J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Jul;42(5):495-515. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2022.2089403. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 35771985 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of bioactive components in Ferula assafo dried oleo-gum resin and assessment of its protective function against cadmium-induced oxidative damage, genotoxicity, and cytotoxicity in rats.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Dec 12;14:101853. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101853. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39758803 Free PMC article.
-
Shikimic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 8;15(1):8126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90549-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40057537 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins Ameliorate Cadmium-Induced Senescence of Osteocytes Through Combating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;13(12):1515. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121515. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765843 Free PMC article.
-
Colpomenia sinuosa extract mitigates lead acetate-induced testicular dysfunctions in male rats.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Apr 28;12:1551773. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1551773. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40356721 Free PMC article.
-
Annona squamosa Fruit Extract Ameliorates Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular Injury by Modulating JAK-1/STAT-3/SOCS-1 Signaling in Male Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 20;25(10):5562. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105562. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Baqami N. M., Hamza R. Z. (2021). Protective effect of resveratrol against hepatotoxicity of cadmium in male rats: antioxidant and histopathological approaches. Coatings 11 (5), 594–611. 10.3390/coatings11050594 - DOI
-
- Almeer R. S., Alarifi S., Alkahtani S., Ibrahim S. R., Ali D., Moneim A. (2018). The potential hepatoprotective effect of royal jelly against cadmium chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is mediated by suppression of oxidative stress and upregulation of Nrf2 expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 106, 1490–1498. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.089 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Tameme H. J., Hadi M. Y., Hameed I. H. (2015). Phytochemical analysis of Urtica dioica leaves by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharmacog. Phytother. 7 (10), 238–252. 10.5897/JPP2015.0361 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

