Histidine-rich glycoprotein in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis-related disease progression and liver carcinogenesis
- PMID: 38469298
- PMCID: PMC10925642
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342404
Histidine-rich glycoprotein in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis-related disease progression and liver carcinogenesis
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. In 20%-30% of MASLD patients, the disease progresses to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, previously NASH) which can lead to fibrosis/cirrhosis, liver failure as well as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here we investigated the role of histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG), a plasma protein produced by hepatocytes, in MASLD/MASH progression and HCC development.
Methods: The role of HRG was investigated by morphological, cellular, and molecular biology approaches in (a) HRG knock-out mice (HRG-/- mice) fed on a CDAA dietary protocol or a MASH related diethyl-nitrosamine/CDAA protocol of hepatocarcinogenesis, (b) THP1 monocytic cells treated with purified HRG, and (c) well-characterized cohorts of MASLD patients with or without HCC.
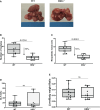
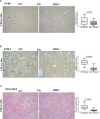
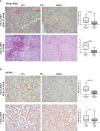
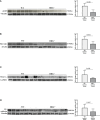
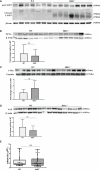
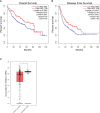
Results: In non-neoplastic settings, murine and clinical data indicate that HRG increases significantly in parallel with disease progression. In particular, in MASLD/MASH patients, higher levels of HRG plasma levels were detected in subjects with extensive fibrosis/cirrhosis. When submitted to the pro-carcinogenic protocol, HRG-/- mice showed a significant decrease in the volume and number of HCC nodules in relation to decreased infiltration of macrophages producing pro-inflammatory mediators, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-10, and VEGF as well as impaired angiogenesis. The histopathological analysis (H-score) of MASH-related HCC indicate that the higher HRG positivity in peritumoral tissue significantly correlates with a lower overall patient survival and an increased recurrence. Moreover, a significant increase in HRG plasma levels was detected in cirrhotic (F4) patients and in patients carrying HCC vs. F0/F1 patients.
Conclusion: Murine and clinical data indicate that HRG plays a significant role in MASLD/MASH progression to HCC by supporting a specific population of tumor-associated macrophages with pro-inflammatory response and pro-angiogenetic capabilities which critically support cancer cell survival. Furthermore, our data suggest HRG as a possible prognostic predictor in HCC patients with MASLD/MASH-related HCCs.
Keywords: HCC; MASH; chronic liver diseases; fibrogenesis; hepatocellular carcinoma; histidine-rich glycoprotein; inflammation; liver carcinogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Foglia, Sutti, Cannito, Rosso, Maggiora, Casalino, Bocca, Novo, Protopapa, Ramavath, Provera, Gambella, Bugianesi, Tacke, Albano and Parola.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

