Bi-specific autoantigen-T cell engagers as targeted immunotherapy for autoreactive B cell depletion in autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 38469301
- PMCID: PMC10926275
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335998
Bi-specific autoantigen-T cell engagers as targeted immunotherapy for autoreactive B cell depletion in autoimmune diseases
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Bi-specific autoantigen-T cell engagers as targeted immunotherapy for autoreactive B cell depletion in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1543066. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1543066. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39850882 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: In autoimmune diseases, autoreactive B cells comprise only the 0.1-0.5% of total circulating B cells. However, current first-line treatments rely on non-specific and general suppression of the immune system, exposing patients to severe side effects. For this reason, identification of targeted therapies for autoimmune diseases is an unmet clinical need.
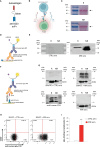
Methods: Here, we designed a novel class of immunotherapeutic molecules, Bi-specific AutoAntigen-T cell Engagers (BiAATEs), as a potential approach for targeting the small subset of autoreactive B cells. To test this approach, we focused on a prototype autoimmune disease of the kidney, membranous nephropathy (MN), in which phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) serves as primary nephritogenic antigen. Specifically, we developed a BiAATE consisting of the immunodominant Cysteine-Rich (CysR) domain of PLA2R and the single-chain variable fragment (scFv) of an antibody against the T cell antigen CD3, connected by a small flexible linker.
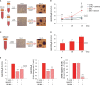
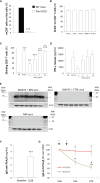
Results: BiAATE creates an immunological synapse between autoreactive B cells bearing an CysR-specific surface Ig+ and T cells. Ex vivo, the BiAATE successfully induced T cell-dependent depletion of PLA2R-specific B cells isolated form MN patients, sparing normal B cells. Systemic administration of BiAATE to mice transgenic for human CD3 reduced anti-PLA2R antibody levels following active immunization with PLA2R.
Discussion: Should this approach be confirmed for other autoimmune diseases, BiAATEs could represent a promising off-the-shelf therapy for precision medicine in virtually all antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases for which the pathogenic autoantigen is known, leading to a paradigm shift in the treatment of these diseases.
Keywords: anti-PLA2R antibodies; autoimmune diseases; autoreactive B cell; bi-specific autoantigen-T cell engagers; membranous nephropathy; targeted immunotherapies.
Copyright © 2024 Perico, Casiraghi, Sônego, Todeschini, Corna, Cerullo, Pezzotta, Isnard-Petit, Faravelli, Forneris, Thiam, Benigni and Remuzzi.
Conflict of interest statement
FS, PI-P and KT were employed by genOway. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

