Role of β-cell autophagy in β-cell physiology and the development of diabetes
- PMID: 38470018
- PMCID: PMC11143416
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.14184
Role of β-cell autophagy in β-cell physiology and the development of diabetes
Abstract
Elucidating the molecular mechanism of autophagy was a landmark in understanding not only the physiology of cells and tissues, but also the pathogenesis of diverse diseases, including diabetes and metabolic disorders. Autophagy of pancreatic β-cells plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of the mass, structure and function of β-cells, whose dysregulation can lead to abnormal metabolic profiles or diabetes. Modulators of autophagy are being developed to improve metabolic profile and β-cell function through the removal of harmful materials and rejuvenation of organelles, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Among the known antidiabetic drugs, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists enhance the autophagic activity of β-cells, which might contribute to the profound effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on systemic metabolism. In this review, the results from studies on the role of autophagy in β-cells and their implication in the development of diabetes are discussed. In addition to non-selective (macro)autophagy, the role and mechanisms of selective autophagy and other minor forms of autophagy that might occur in β-cells are discussed. As β-cell failure is the ultimate cause of diabetes and unresponsiveness to conventional therapy, modulation of β-cell autophagy might represent a future antidiabetic treatment approach, particularly in patients who are not well managed with current antidiabetic therapy.
Keywords: Autophagy; Lysosome; β‐Cells.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures


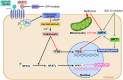
Similar articles
-
β-cell autophagy: Mechanism and role in β-cell dysfunction.Mol Metab. 2019 Sep;27S(Suppl):S92-S103. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.06.014. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31500836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic β-Cells, Diabetes and Autophagy.Endocr Res. 2025 Feb;50(1):12-27. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2024.2413064. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Endocr Res. 2025. PMID: 39429147 Review.
-
Role of autophagy in the progression from obesity to diabetes and in the control of energy balance.Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Feb;36(2):223-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0024-7. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Arch Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23371805 Review.
-
Role of islet β cell autophagy in the pathogenesis of diabetes.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Dec;25(12):620-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.08.005. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25242548 Review.
-
Role of autophagy in diabetes and endoplasmic reticulum stress of pancreatic β-cells.Exp Mol Med. 2012 Feb 29;44(2):81-8. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.030. Exp Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22257883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing metformin efficacy with cholecalciferol and taurine in diabetes therapy: Potential and limitations.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jan 15;16(1):100066. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i1.100066. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39817227 Free PMC article.
-
The role of autophagy in pancreatic diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1444657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444657. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39403146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and inflammation an intricate affair in the management of obesity and metabolic disorders: evidence for novel pharmacological strategies?Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1407336. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407336. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38895630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

