Human norovirus cultivation systems and their use in antiviral research
- PMID: 38470106
- PMCID: PMC11019851
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01663-23
Human norovirus cultivation systems and their use in antiviral research
Abstract
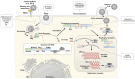
Human norovirus (HuNoV) is a major cause of acute gastroenteritis and foodborne diseases, affecting all age groups. Despite its clinical needs, no approved antiviral therapies are available. Since the discovery of HuNoV in 1972, studies on anti-norovirals, mechanism of HuNoV infection, viral inactivation, etc., have been hampered by the lack of a robust laboratory-based cultivation system for HuNoV. A recent breakthrough in the development of HuNoV cultivation systems has opened opportunities for researchers to investigate HuNoV biology in the context of de novo HuNoV infections. A tissue stem cell-derived human intestinal organoid/enteroid (HIO) culture system is one of those that supports HuNoV replication reproducibly and, to our knowledge, is most widely distributed to laboratories worldwide to study HuNoV and develop therapeutic strategies. This review summarizes recently developed HuNoV cultivation systems, including HIO, and their use in antiviral studies.
Keywords: antiviral study; human norovirus; intestinal organoid; laboratory cultivation system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- CDC . 2023. Norovirus Burden and Trends. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/burden.html. Retrieved Feb 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP20H00259, JP23K18381/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23K18381, JP21H02743/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23fk0108669/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP23fk0108667/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

