Sarcomeric tropomyosin expression during human iPSC differentiation into cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 38470291
- PMCID: PMC11566289
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21850
Sarcomeric tropomyosin expression during human iPSC differentiation into cardiomyocytes
Abstract
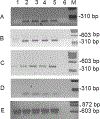
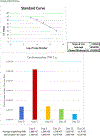
Tropomyosin (TPM) is an essential sarcomeric component, stabilizing the thin filament and facilitating actin's interaction with myosin. In mammals, including humans, there are four TPM genes (TPM1, TPM2, TPM3, and TPM4) each of which generates a multitude of TPM isoforms via alternative splicing and using different promoters. In this study, we have examined the expression of transcripts as well as proteins of various sarcomeric TPM isoforms during human inducible pluripotent stem cell differentiation into cardiomyocytes. During the differentiation time course, we harvested cells on Days 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 to analyze for various sarcomeric TPM transcripts by qRT-PCR and for sarcomeric TPM proteins using two-dimensional Western blot with sarcomeric TPM-specific CH1 monoclonal antibody followed by mass spectra analyses. Our results show increasing levels of total TPM transcripts and proteins during the period of differentiation, but varying levels of specific TPM isoforms during the same period. By Day 20, the rank order of TPM transcripts was TPM1α > TPM1κ > TPM2α > TPM1μ > TPM3α > TPM4α. TPM1α was the dominant protein produced with some TPM2 and much less TPM1κ and μ. Interestingly, small amounts of two lower molecular weight TPM3 isoforms were detected on Day 15. To the best of our knowledge this is the first demonstration of TPM1μ non-muscle isoform protein expression before and during cardiac differentiation.
Keywords: LC‐MS/MS; TPM1α; TPM1μ; hiPSC‐derived cardiomyocytes; qRT‐PCR.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
No, there is no conflict of interest
Figures














Similar articles
-
Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of TPM transcripts and proteins in developing striated chicken muscles indicate TPM4α is the major sarcomeric cardiac tropomyosin from early embryonic life to adulthood.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2018 Oct;75(10):437-449. doi: 10.1002/cm.21495. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 30255988 Free PMC article.
-
Tropomyosin Isoform Diversity in the Cynomolgus Monkey Heart and Skeletal Muscles Compared to Human Tissues.Biochem Res Int. 2023 Jan 24;2023:1303500. doi: 10.1155/2023/1303500. eCollection 2023. Biochem Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36733713 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of various sarcomeric tropomyosin isoforms in equine striated muscles.Open Vet J. 2017;7(2):180-191. doi: 10.4314/ovj.v7i2.17. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Open Vet J. 2017. PMID: 28717602 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Screening and validation of key microRNAs regulating muscle development in Hanper sheep.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 12;20(6):e0325054. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325054. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40504789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bang ML, Chen J (2015) Roles of nebulin family members in the heart. Circulation J 79: 2081–2087. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

