Effectiveness of Nonpharmacological Behavioural Interventions in Managing Dental Fear and Anxiety among Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38470648
- PMCID: PMC10931341
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12050537
Effectiveness of Nonpharmacological Behavioural Interventions in Managing Dental Fear and Anxiety among Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-pharmacological behavioural interventions (NPBIs) have been employed by dentists to alleviate dental fear and anxiety (DFA) among preschool and school children. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to investigate the effectiveness of different NPBIs in reducing DFA among children aged below 12.
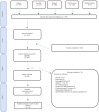
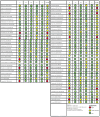
Method: A comprehensive search was conducted using four electronic databases to identify randomised controlled trials that assess the effectiveness of NPBIs among preschool and school children. Two reviewers independently screened and selected the relevant studies, evaluated the risk of bias, and extracted relevant data for qualitative and quantitative syntheses.
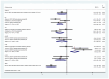
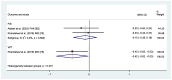
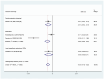
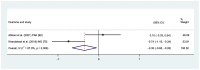
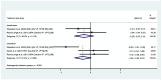
Result: A total of 66 articles were included in the study. Except during more invasive dental procedures, the use of distraction techniques was found to result in significantly lower self-rated anxiety, better cooperation, and lower pulse rate compared to the tell-show-do method. However, inconsistent results were reported regarding the efficacy of virtual reality, modelling, visual pedagogies, tell-show-do and other NPBIs in reducing DFA among children.
Conclusions: The studies exhibited substantial heterogeneity due to varying age groups, methods of implementing NPBIs, dental treatments performed, and measurement scales employed in the evaluation of DFA.
Keywords: anxiety management; dental anxiety; nonpharmacological intervention; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Audio and Audio-Visual Distraction Aids for Management of Pain and Anxiety in Children and Adults Undergoing Dental Treatment- A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Mar 1;46(2):86-106. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-46.2.2. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35533223
-
Effectiveness of music interventions on dental anxiety in paediatric and adult patients: a systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011;9(18):588-630. doi: 10.11124/01938924-201109180-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 27819961
-
Non-pharmacological management of dental fear and anxiety in children and adolescents: An umbrella review.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2022 Sep;23(3):230-242. doi: 10.23804/ejpd.2022.23.03.11. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 36172904
-
Evidence of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for the management of dental fear in paediatric dentistry: a systematic review protocol.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 18;7(8):e016043. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016043. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28821522 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of dental treatments under nitrous oxide-oxygen inhalation sedation in pediatric patients with dental anxiety: a 10-Year retrospective study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 16;25(1):1171. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06588-w. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40670963 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Nonpharmacological Behavior Management in Children With Dental Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;8(8):e71176. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71176. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40843385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary Cortisol as a Biomarker for Assessing Fear and Anxiety in Patients with Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 17;15(4):489. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15040489. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002640 Free PMC article.
-
Culture and Behaviour Management of Children in the Dental Clinic: A Scoping Review.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;13(5):186. doi: 10.3390/dj13050186. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectious Diseases-Approved Virtual Reality Goggles for Common Procedures in Pediatric Surgical Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 20;13(18):5572. doi: 10.3390/jcm13185572. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39337059 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

