Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation to Treat Neuropathic Pain: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 38470666
- PMCID: PMC10930707
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12050555
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation to Treat Neuropathic Pain: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
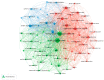
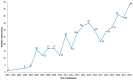
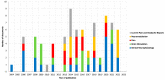
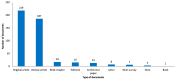
Neuropathic pain is caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory system and is one of the most incapacitating pain types, representing a significant non-met medical need. Due to the increase in research in the field and since innovative therapeutic strategies are required, namely in intractable neuropathic pain, neurostimulation has been used. Within this approach, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) that uses a transient magnetic field to produce electrical currents over the cortex emerges as a popular method in the literature. Since this is an area in expansion and due to the putative role of TMS, we performed a bibliometric analysis in Scopus with the primary objective of identifying the scientific production related to the use of TMS to manage neuropathic pain. The research had no restrictions, and the analysis focused on the characteristics of the literature retrieved, scientific collaboration and main research topics from inception to 6 July 2023. A total of 474 articles were collected. A biggest co-occurrence between the terms "neuropathic pain" and "transcranial magnetic stimulation" was obtained. The journal "Clinical Neurophysiology" leads the Top 5 most productive sources. The United States is the most productive country, with 50% of US documents being "review articles", followed by France, with 56% of French documents being "original articles". Lefaucheur, JP and Saitoh, Y are the two most influential authors. The most frequent type of document was "original article". Most of the studies (34%) that identified the neuropathic pain type focused on traumatic neuropathic pain, although a large proportion (38%) did not report the neuropathic pain type. This study allows us to provide a general overview of the field of TMS application for neuropathic pain and is useful for establishing future directions of research in this field.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; neuropathic pain; pain; transcranial magnetic stimulation; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research Hotspots and Effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Pain: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Jun 21;16:887246. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.887246. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35814960 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring research trends and focal points in the application of transcranial magnetic stimulation for enhancing motor function in post-stroke patients: A bibliometric and content analytical approach.Injury. 2023 Dec;54(12):111116. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2023.111116. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Injury. 2023. PMID: 37880033
-
Non-invasive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) of the Motor Cortex for Neuropathic Pain-At the Tipping Point?Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2013 Oct 29;4(4):e0023. doi: 10.5041/RMMJ.10130. eCollection 2013. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2013. PMID: 24228166 Free PMC article.
-
Pain and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: A Bibliometric Analysis.J Pain Res. 2023 Nov 1;16:3655-3671. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S427658. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37933296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Treating Chronic Neuropathic Pain: a Systematic Review.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021 May 12;25(7):48. doi: 10.1007/s11916-021-00960-5. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021. PMID: 33978846
Cited by
-
Dual-target peripheral and central magnetic stimulation for rehabilitation of chronic pelvic pain syndrome associated with psychosomatic symptoms: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 17;20(7):e0326740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326740. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40674346 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Clinical Learning Environment for Nursing and Midwifery Education.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Oct 30;17:4973-4987. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S486321. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39492982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Treede R.D., Jensen T.S., Campbell J.N., Cruccu G., Dostrovsky J.O., Griffin J.W., Hansson P., Hughes R., Nurmikko T., Serra J. Neuropathic pain: Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008;70:1630–1635. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Finnerup N.B., Haroutounian S., Kamerman P., Baron R., Bennett D.L., Bouhassira D., Cruccu G., Freeman R., Hansson P., Nurmikko T., et al. Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain. 2016;157:1599–1606. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Treede R.-D., Rief W., Barke A., Aziz Q., Bennett M.I., Benoliel R., Cohen M., Evers S., Finnerup N.B., First M.B., et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) Pain. 2019;160:19–27. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001384. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

