Measuring Motivations to Eat Palatable Foods: Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Italian Version of the Palatable Eating Motives Scale (PEMS-IT)
- PMID: 38470685
- PMCID: PMC10930930
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12050574
Measuring Motivations to Eat Palatable Foods: Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Italian Version of the Palatable Eating Motives Scale (PEMS-IT)
Abstract
Background: Gaining knowledge of the various reasons behind people's consumption of highly processed foods has the potential to enhance obesity prevention initiatives and open avenues to tailor treatment approaches for obesity and binge eating at a more personalized level. This contribution aimed to test the psychometric properties and factor structure of the Palatable Eating Motives Scale (PEMS-IT) in a community sample of Italian adults.
Methods: A confirmatory factor analysis was performed to test the factor structure of the Italian version of the PEMS (PEMS-IT) on a total of 616 respondents. Furthermore, the reliability and convergent validity analysis of the tool were evaluated.
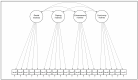
Results: The analysis confirmed the four-factor structure of PEMS-IT [(YBχ2 (164) = 537.901; p < 0.001, the CFI = 0.918, RMSEA = 0.072; 90%CI [0.065-0.078]; p(RMSEA < 0.05) < 0.001, and SRMR = 0.080] and satisfactory reliability on its subscales (Cronbach's α: 0.745-0.917). Positive correlations were also found with food addiction and binge-eating symptoms, compulsive eating behavior, and uncontrolled and emotional eating.
Conclusions: The PEMS-IT appears to be an instrument with promising psychometric properties and potential applications in clinical settings. However, it also has some limitations, and future studies could focus on improving the semantic content of the elements to increase the overall utility and precision of the instrument.
Keywords: eating behaviors; eating disorders; food addiction; motivation; palatable foods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Castelnuovo G., Manzoni G.M., Villa V., Cesa G.L., Pietrabissa G., Molinari E. The STRATOB study: Design of a randomized controlled clinical trial of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Brief Strategic Therapy with telecare in patients with obesity and binge-eating disorder referred to residential nutritional rehabilitation. Trials. 2011;12:114. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous