Unveiling the MIL-53(Al) MOF: Tuning Photoluminescence and Structural Properties via Volatile Organic Compounds Interactions
- PMID: 38470719
- PMCID: PMC10935077
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14050388
Unveiling the MIL-53(Al) MOF: Tuning Photoluminescence and Structural Properties via Volatile Organic Compounds Interactions
Abstract
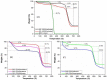
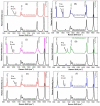
MIL-53(Al) is a metal-organic framework (MOF) with unique properties, including structural flexibility, thermal stability, and luminescence. Its ability to adsorb volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and water vapor makes it a promising platform for sensing applications. This study investigated the adsorption mechanism of MIL-53(Al) with different VOCs, including ketones, alcohols, aromatics, and water molecules, focusing on structural transformations due to pore size variation and photoluminescence properties. The reported results assess MIL-53(Al) selectivity towards different VOCs and provide insights into their fundamental properties and potential applications in sensing.
Keywords: MIL-53(Al); Metal-Organic Frameworks; VOCs; guest-adsorption; photoluminescence; structural transitions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Specific Recognition and Adsorption of Volatile Organic Compounds by Using MIL-125-Based Porous Fluorescence Probe Material.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;13(19):2732. doi: 10.3390/nano13192732. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836373 Free PMC article.
-
Stimuli-responsive photoluminescent and structural properties of MIL-53(Al) MOF for sensing applications.J Phys Condens Matter. 2024 May 9;36(31). doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ad43a4. J Phys Condens Matter. 2024. PMID: 38663409
-
Adsorption of volatile organic compounds by metal-organic frameworks MIL-101: influence of molecular size and shape.J Hazard Mater. 2011 Nov 15;195:124-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.020. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Hazard Mater. 2011. PMID: 21871718
-
Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) Derivatives as Promising Chemiresistive Gas Sensing Materials: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 1;20(5):4388. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054388. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36901399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adsorption and Degradation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): A Review.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 2;15(21):7727. doi: 10.3390/ma15217727. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metal-Organic-Framework-Based Optical Biosensors: Recent Advances in Pathogen Detection and Environmental Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Aug 15;25(16):5081. doi: 10.3390/s25165081. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40871944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering MIL-53(Al) MOF with Carbon Dots for Synergistic Photocatalysis Applications in Organic Dye Degradation.ACS Omega. 2025 Apr 30;10(18):18527-18538. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11113. eCollection 2025 May 13. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40385199 Free PMC article.
-
Microwaves induced epitaxial growth of urchin like MIL-53(Al) crystals on ceramic supports.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 29;14(1):20067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71150-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39209977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiao L., Seow J.Y.R., Skinner W.S., Wang Z.U., Jiang H.-L. Metal–organic frameworks: Structures and functional applications. Mater. Today. 2019;27:43–68. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2018.10.038. - DOI
-
- Kumar P., Vellingiri K., Kim K.-H., Brown R.J., Manos M.J. Modern progress in metal-organic frameworks and their composites for diverse applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017;253:251–265. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.07.003. - DOI
-
- Safaei M., Foroughi M.M., Ebrahimpoor N., Jahani S., Omidi A., Khatami M. A review on metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019;118:401–425. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

