Engineered Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 38470744
- PMCID: PMC10935217
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14050413
Engineered Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
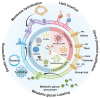
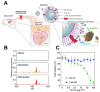
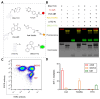
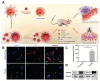
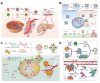
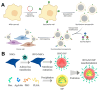
Recent strides in nanomaterials science have paved the way for the creation of reliable, effective, highly accurate, and user-friendly biomedical systems. Pioneering the integration of natural cell membranes into sophisticated nanocarrier architectures, cell membrane camouflage has emerged as a transformative approach for regulated drug delivery, offering the benefits of minimal immunogenicity coupled with active targeting capabilities. Nevertheless, the utility of nanomaterials with such camouflage is curtailed by challenges like suboptimal targeting precision and lackluster therapeutic efficacy. Tailored cell membrane engineering stands at the forefront of biomedicine, equipping nanoplatforms with the capacity to conduct more complex operations. This review commences with an examination of prevailing methodologies in cell membrane engineering, spotlighting strategies such as direct chemical modification, lipid insertion, membrane hybridization, metabolic glycan labeling, and genetic engineering. Following this, an evaluation of the unique attributes of various nanomaterials is presented, delivering an in-depth scrutiny of the substantial advancements and applications driven by cutting-edge engineered cell membrane camouflage. The discourse culminates by recapitulating the salient influence of engineered cell membrane camouflage within nanomaterial applications and prognosticates its seminal role in transformative healthcare technologies. It is envisaged that the insights offered herein will catalyze novel avenues for the innovation and refinement of engineered cell membrane camouflaged nanotechnologies.
Keywords: active targeting; biomedical applications; cell membrane-camouflaged nanomaterials; engineered cell membrane; long circulation time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Huang L.L., Wu H.H., Xu D.H., Gao J.Q. Recent advances of cell membrane-derived biomimetic nanotechnology in cancer targeted drug delivery system. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2022;57:85–97.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

