Cheminformatics-Guided Cell-Free Exploration of Peptide Natural Products
- PMID: 38470819
- PMCID: PMC11151186
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c11306
Cheminformatics-Guided Cell-Free Exploration of Peptide Natural Products
Abstract
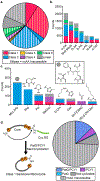
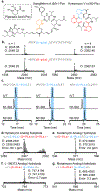
There have been significant advances in the flexibility and power of in vitro cell-free translation systems. The increasing ability to incorporate noncanonical amino acids and complement translation with recombinant enzymes has enabled cell-free production of peptide-based natural products (NPs) and NP-like molecules. We anticipate that many more such compounds and analogs might be accessed in this way. To assess the peptide NP space that is directly accessible to current cell-free technologies, we developed a peptide parsing algorithm that breaks down peptide NPs into building blocks based on ribosomal translation logic. Using the resultant data set, we broadly analyze the biophysical properties of these privileged compounds and perform a retrobiosynthetic analysis to predict which peptide NPs could be directly synthesized in augmented cell-free translation reactions. We then tested these predictions by preparing a library of highly modified peptide NPs. Two macrocyclases, PatG and PCY1, were used to effect the head-to-tail macrocyclization of candidate NPs. This retrobiosynthetic analysis identified a collection of high-priority building blocks that are enriched throughout peptide NPs, yet they had not previously been tested in cell-free translation. To expand the cell-free toolbox into this space, we established, optimized, and characterized the flexizyme-enabled ribosomal incorporation of piperazic acids. Overall, these results demonstrate the feasibility of cell-free translation for peptide NP total synthesis while expanding the limits of the technology. This work provides a novel computational tool for exploration of peptide NP chemical space, that could be expanded in the future to allow design of ribosomal biosynthetic pathways for NPs and NP-like molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): A.T. and E.N.M. are co-founders of Predictive, LLC, which develops computational methodologies and software for toxicity prediction. All other authors declare they have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of an anthraquinone and chalcone derivatives-based virtual combinatorial library. A cheminformatics "proof-of-concept" study.J Mol Graph Model. 2022 Dec;117:108307. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2022.108307. Epub 2022 Aug 15. J Mol Graph Model. 2022. PMID: 36096064
-
An expanded set of amino acid analogs for the ribosomal translation of unnatural peptides.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 3;2(10):e972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000972. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17912351 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthetic Strategies for Macrocyclic Peptides.Molecules. 2021 Jun 1;26(11):3338. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113338. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34206124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Macrocyclic Peptide Families from Combinatorial Libraries Containing Noncanonical Amino Acids Using Cheminformatics and Bioinformatics Inspired Clustering.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Jun 16;18(6):1425-1434. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00159. Epub 2023 May 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37220419 Free PMC article.
-
Principle and design of pseudo-natural products.Nat Chem. 2020 Mar;12(3):227-235. doi: 10.1038/s41557-019-0411-x. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Nat Chem. 2020. PMID: 32015480 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of a head-to-tail peptide cyclase to prepare hybrid RiPPs.Chem Commun (Camb). 2024 Jun 20;60(51):6508-6511. doi: 10.1039/d3cc04919a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38833296 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free synthetic biology for natural product biosynthesis and discovery.Chem Soc Rev. 2025 May 6;54(9):4314-4352. doi: 10.1039/d4cs01198h. Chem Soc Rev. 2025. PMID: 40104998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Modification and Membrane Localization of Proteins in Cell-Free System.ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Jul 18;14(7):2729-2738. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00155. Epub 2025 Jun 19. ACS Synth Biol. 2025. PMID: 40536220 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Aquatic Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Marine Metagenomes Using a High-Throughput Screening Approach.Mar Drugs. 2025 Apr 20;23(4):178. doi: 10.3390/md23040178. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40278299 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and engineering post-translational modifications with high-throughput cell-free expression.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 5;16(1):7215. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60526-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40764296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ling LL; Schneider T; Peoples AJ; Spoering AL; Engels I; Conlon BP; Mueller A; Schäberle TF; Hughes DE; Epstein S; Jones M; Lazarides L; Steadman VA; Cohen DR; Felix CR; Fetterman KA; Millett WP; Nitti AG; Zullo AM; Chen C; Lewis K A New Antibiotic Kills Pathogens without Detectable Resistance. Nature 2015, 517 (7535), 455–459. DOI: 10.1038/nature14098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Imai Y; Meyer KJ; Iinishi A; Favre-Godal Q; Green R; Manuse S; Caboni M; Mori M; Niles S; Ghiglieri M; Honrao C; Ma X; Guo JJ; Makriyannis A; Linares-Otoya L; Böhringer N; Wuisan ZG; Kaur H; Wu R; Mateus A; Typas A; Savitski MM; Espinoza JL; O’Rourke A; Nelson KE; Hiller S; Noinaj N; Schäberle TF; D’Onofrio A; Lewis K A New Antibiotic Selectively Kills Gram-Negative Pathogens. Nature 2019, 576 (7787), 459–464. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1791-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnison PG; Bibb MJ; Bierbaum G; Bowers AA; Bugni TS; Bulaj G; Camarero JA; Campopiano DJ; Challis GL; Clardy J; Cotter PD; Craik DJ; Dawson M; Dittmann E; Donadio S; Dorrestein PC; Entian K-D; Fischbach MA; Garavelli JS; Göransson U; Gruber CW; Haft DH; Hemscheidt TK; Hertweck C; Hill C; Horswill AR; Jaspars M; Kelly WL; Klinman JP; Kuipers OP; Link AJ; Liu W; Marahiel MA; Mitchell DA; Moll GN; Moore BS; Müller R; Nair SK; Nes IF; Norris GE; Olivera BM; Onaka H; Patchett ML; Piel J; Reaney MJT; Rebuffat S; Ross RP; Sahl H-G; Schmidt EW; Selsted ME; Severinov K; Shen B; Sivonen K; Smith L; Stein T; Süssmuth RD; Tagg JR; Tang G-L; Truman AW; Vederas JC; Walsh CT; Walton JD; Wenzel SC; Willey JM; van der Donk WA Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptide Natural Products: Overview and Recommendations for a Universal Nomenclature. Nat. Prod. Rep 2013, 30 (1), 108–160. DOI: 10.1039/c2np20085f. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

