Gut Microbiota-Tryptophan Metabolism-GLP-1 Axis Participates in β-Cell Regeneration Induced by Dapagliflozin
- PMID: 38471012
- PMCID: PMC11109800
- DOI: 10.2337/db23-0553
Gut Microbiota-Tryptophan Metabolism-GLP-1 Axis Participates in β-Cell Regeneration Induced by Dapagliflozin
Abstract
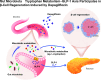
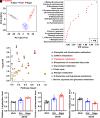
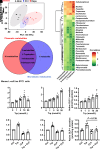
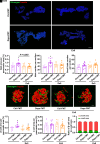
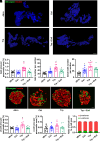
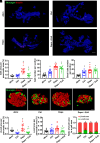
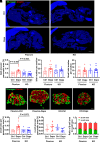
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, efficacious antidiabetic agents that have cardiovascular and renal benefits, can promote pancreatic β-cell regeneration in type 2 diabetic mice. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to use multiomics to identify the mediators involved in β-cell regeneration induced by dapagliflozin. We showed that dapagliflozin lowered blood glucose level, upregulated plasma insulin level, and increased islet area in db/db mice. Dapagliflozin reshaped gut microbiota and modulated microbiotic and plasmatic metabolites related to tryptophan metabolism, especially l-tryptophan, in the diabetic mice. Notably, l-tryptophan upregulated the mRNA level of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) production-related gene (Gcg and Pcsk1) expression and promoted GLP-1 secretion in cultured mouse intestinal L cells, and it increased the supernatant insulin level in primary human islets, which was eliminated by GPR142 antagonist. Transplant of fecal microbiota from dapagliflozin-treated mice, supplementation of l-tryptophan, or treatment with dapagliflozin upregulated l-tryptophan, GLP-1, and insulin or C-peptide levels and promoted β-cell regeneration in db/db mice. Addition of exendin 9-39, a GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) antagonist, or pancreatic Glp1r knockout diminished these beneficial effects. In summary, treatment with dapagliflozin in type 2 diabetic mice promotes β-cell regeneration by upregulating GLP-1 production, which is mediated via gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolism.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J 2020;41:255–323 - PubMed
-
- Koepsell H. The Na+-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 are targets for the treatment of diabetes and cancer. Pharmacol Ther 2017;170:148–165 - PubMed
-
- Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, et al.; DECLARE–TIMI 58 Investigators . Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;380:347–357 - PubMed
-
- Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, et al.; CREDENCE Trial Investigators . Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2295–2306 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Talent Project of Clinical Key Project of Peking University Third Hospital
- 82070319/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- the National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Program, P. R. China (2023)
- PKU2023LCXQ025/Clinical Medicine Plus X-Young Scholars Project of Peking University
- 7222216/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

