Catalytic residues of microRNA Argonautes play a modest role in microRNA star strand destabilization in C. elegans
- PMID: 38471816
- PMCID: PMC11109956
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae170
Catalytic residues of microRNA Argonautes play a modest role in microRNA star strand destabilization in C. elegans
Abstract
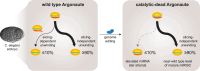
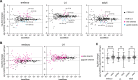
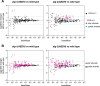
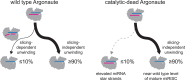
Many microRNA (miRNA)-guided Argonaute proteins can cleave RNA ('slicing'), even though miRNA-mediated target repression is generally cleavage-independent. Here we use Caenorhabditis elegans to examine the role of catalytic residues of miRNA Argonautes in organismal development. In contrast to previous work, mutations in presumed catalytic residues did not interfere with development when introduced by CRISPR. We find that unwinding and decay of miRNA star strands is weakly defective in the catalytic residue mutants, with the largest effect observed in embryos. Argonaute-Like Gene 2 (ALG-2) is more dependent on catalytic residues for unwinding than ALG-1. The miRNAs that displayed the greatest (albeit minor) dependence on catalytic residues for unwinding tend to form stable duplexes with their star strand, and in some cases, lowering duplex stability alleviates dependence on catalytic residues. While a few miRNA guide strands are reduced in the mutant background, the basis of this is unclear since changes were not dependent on EBAX-1, an effector of Target-Directed miRNA Degradation (TDMD). Overall, this work defines a role for the catalytic residues of miRNA Argonautes in star strand decay; future work should examine whether this role contributes to the selection pressure to conserve catalytic activity of miRNA Argonautes across the metazoan phylogeny.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research 2024.
Figures
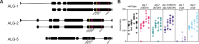
Update of
-
The catalytic activity of microRNA Argonautes plays a modest role in microRNA star strand destabilization in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 9:2023.01.19.524782. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.19.524782. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):4985-5001. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae170. PMID: 36711716 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
The catalytic activity of microRNA Argonautes plays a modest role in microRNA star strand destabilization in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 9:2023.01.19.524782. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.19.524782. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):4985-5001. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae170. PMID: 36711716 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The slicing activity of miRNA-specific Argonautes is essential for the miRNA pathway in C. elegans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov 1;40(20):10452-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks748. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22904066 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the contribution of microRNA-specific Argonautes with slicer capability in animals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):5002-5015. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae173. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38477356 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA strand selection: Unwinding the rules.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 May;12(3):e1627. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1627. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 32954644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology and Mechanisms of Short RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Genet. 2013;83:1-69. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407675-4.00001-8. Adv Genet. 2013. PMID: 23890211 Review.
Cited by
-
What goes up must come down: off switches for regulatory RNAs.Genes Dev. 2024 Aug 20;38(13-14):597-613. doi: 10.1101/gad.351934.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39111824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A lncRNA drives developmentally-timed decay of all members of an essential microRNA family.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 31:2025.07.30.667716. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.30.667716. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766674 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Recent advances in understanding microRNA function and regulation in C. elegans.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 15;154(Pt A):4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.03.011. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 37055330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A noncanonical Pol III-dependent, Microprocessor-independent biogenesis pathway generates a germline enriched miRNA family.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 2:2025.04.11.648421. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.11.648421. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Genes Dev. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1101/gad.352481.124. PMID: 40501874 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Tabara H., Sarkissian M., Kelly W.G., Fleenor J., Grishok A., Timmons L., Fire A., Mello C.C. The rde-1 gene, RNA interference, and transposon silencing in C. elegans. Cell. 1999; 99:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Grishok A., Pasquinelli A.E., Conte D., Li N., Parrish S., Ha I., Baillie D.L., Fire A., Ruvkun G., Mello C.C. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell. 2001; 106:23–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

