Breaking tolerance: the autoimmune aspect of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38472321
- PMCID: PMC11682649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-024-01010-y
Breaking tolerance: the autoimmune aspect of atherosclerosis
Abstract
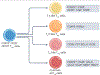
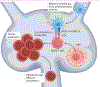
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial walls and is characterized by the accumulation of lipoproteins that are insufficiently cleared by phagocytes. Following the initiation of atherosclerosis, the pathological progression is accelerated by engagement of the adaptive immune system. Atherosclerosis triggers the breakdown of tolerance to self-components. This loss of tolerance is reflected in defective expression of immune checkpoint molecules, dysfunctional antigen presentation, and aberrations in T cell populations - most notably in regulatory T (Treg) cells - and in the production of autoantibodies. The breakdown of tolerance to self-proteins that is observed in ASCVD may be linked to the conversion of Treg cells to 'exTreg' cells because many Treg cells in ASCVD express T cell receptors that are specific for self-epitopes. Alternatively, or in addition, breakdown of tolerance may trigger the activation of naive T cells, resulting in the clonal expansion of T cell populations with pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic effector phenotypes. In this Perspective, we review the evidence that atherosclerosis is associated with a breakdown of tolerance to self-antigens, discuss possible immunological mechanisms and identify knowledge gaps to map out future research. Rational approaches aimed at re-establishing immune tolerance may become game changers in treating ASCVD and in preventing its downstream sequelae, which include heart attacks and strokes.
© 2024. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
K.L. is a co-founder of Atherovax, a biotech company developing a tolerogenic vaccine for atherosclerosis. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tsao CW et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics — 2023 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 147, e93–e621 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Michos ED, McEvoy JW & Blumenthal RS Lipid management for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 381, 1557–1567 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 2195–2207 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

