Inhibition of EHMT1/2 rescues synaptic damage and motor impairment in a PD mouse model
- PMID: 38472451
- PMCID: PMC10933175
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05176-5
Inhibition of EHMT1/2 rescues synaptic damage and motor impairment in a PD mouse model
Abstract
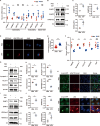
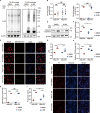
Epigenetic dysregulation that leads to alterations in gene expression and is suggested to be one of the key pathophysiological factors of Parkinson's disease (PD). Here, we found that α-synuclein preformed fibrils (PFFs) induced histone H3 dimethylation at lysine 9 (H3K9me2) and increased the euchromatic histone methyltransferases EHMT1 and EHMT2, which were accompanied by neuronal synaptic damage, including loss of synapses and diminished expression levels of synaptic-related proteins. Furthermore, the levels of H3K9me2 at promoters in genes that encode the synaptic-related proteins SNAP25, PSD95, Synapsin 1 and vGLUT1 were increased in primary neurons after PFF treatment, which suggests a linkage between H3K9 dimethylation and synaptic dysfunction. Inhibition of EHMT1/2 with the specific inhibitor A-366 or shRNA suppressed histone methylation and alleviated synaptic damage in primary neurons that were treated with PFFs. In addition, the synaptic damage and motor impairment in mice that were injected with PFFs were repressed by treatment with the EHMT1/2 inhibitor A-366. Thus, our findings reveal the role of histone H3 modification by EHMT1/2 in synaptic damage and motor impairment in a PFF animal model, suggesting the involvement of epigenetic dysregulation in PD pathogenesis.
Keywords: Histone H3 dimethylation; Motor impairment; Parkinson’s disease; Synaptic dysfunction; α-synuclein preformed fibrils.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Inhibition of EHMT1/2 rescues synaptic and cognitive functions for Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2019 Mar 1;142(3):787-807. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy354. Brain. 2019. PMID: 30668640 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein enhances histone H3 lysine-9 dimethylation and H3K9me2-dependent transcriptional responses.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 3;6:36328. doi: 10.1038/srep36328. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27808254 Free PMC article.
-
Differential patterns of histone methylase EHMT2 and its catalyzed histone modifications H3K9me1 and H3K9me2 during maturation of central auditory system.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Aug;365(2):247-64. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2401-2. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27083448
-
Synaptic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;970:553-72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0932-8_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22351072 Review.
-
Advances in understanding the function of alpha-synuclein: implications for Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2023 Sep 1;146(9):3587-3597. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad150. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37183455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Modifiers: Exploring the Roles of Histone Methyltransferases and Demethylases in Cancer and Neurodegeneration.Biology (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;13(12):1008. doi: 10.3390/biology13121008. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modifications on histone tails in Parkinson's disease.SciBase Neurol. 2024;2(2):1017. Epub 2024 Jul 22. SciBase Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39145143 Free PMC article.
-
PLK2 disrupts autophagic flux to promote SNCA/α-synuclein pathology.Autophagy. 2025 Aug;21(8):1623-1643. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2448914. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Autophagy. 2025. PMID: 39773002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shahmoradian SH, Lewis AJ, Genoud C, Hench J, Moors TE, Navarro PP, Castaño-Díez D, Schweighauser G, Graff-Meyer A, Goldie KN, et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(7):1099–1109. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0423-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

