Association between enthesitis/dactylitis resolution and patient-reported outcomes in guselkumab-treated patients with psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 38472528
- PMCID: PMC11018666
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-024-06921-8
Association between enthesitis/dactylitis resolution and patient-reported outcomes in guselkumab-treated patients with psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the association between enthesitis resolution (ER) and dactylitis resolution (DR) and meaningful improvements in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) among biologic-naïve patients with PsA receiving guselkumab in the DISCOVER-2 study.
Methods: Enthesitis and dactylitis, characteristic lesions of PsA, were evaluated by independent assessors using the Leeds Enthesitis Index (range, 0-6) and Dactylitis Severity Score (range, 0-60). Proportions of patients with ER or DR (score = 0) among those with score > 0 at baseline were determined at weeks 24, 52, and 100. PROs included: fatigue (Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue [FACIT-Fatigue]), pain (0-100 visual analog scale), physical function (Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index [HAQ-DI]), and health-related quality of life (36-item Short-Form Health Survey physical/mental component summary [SF-36 PCS/MCS]). Meaningful responses were defined as: improvements of ≥ 4 for FACIT-Fatigue, ≥ 0.35 for HAQ-DI, and ≥ 5 for SF-36 PCS/MCS and absolute scores of ≤ 15 for minimal pain and ≤ 0.5 for normalized HAQ-DI. Associations between ER/DR status and PRO response status were tested using a Chi-square test.
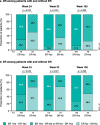
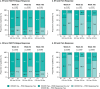
Results: Guselkumab-treated patients with ER were more likely than those without ER to achieve minimal pain (p < 0.001), normalized HAQ-DI (p < 0.001), and PCS response (p < 0.05) at weeks 24, 52, and 100. Patients with DR were more likely than those without DR to achieve FACIT-Fatigue response at week 24 and week 52 (both p ≤ 0.01) and minimal pain at week 24 and normalized HAQ-DI at week 52 (both p ≤ 0.03).
Conclusion: In biologic-naïve patients with active PsA treated with guselkumab, achieving ER or DR was associated with durable improvements in selected PROs, including those of high importance to patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov ( https://clinicaltrials.gov ) NCT03158285; Registered: May 16, 2017. Key Points • At week 100, 65% and 76% of guselkumab-treated patients achieved enthesitis and dactylitis resolution (ER/DR). • Achieving ER was associated with achieving DR and vice versa through the end of study. • Achieving ER or DR was associated with durable and meaningful improvements in selected patient-reported outcomes.
Keywords: Biologic; Dactylitis; Enthesitis; Guselkumab; Psoriatic arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Durable control of psoriatic arthritis with guselkumab across domains and patient characteristics: post hoc analysis of a phase 3 study.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;43(8):2551-2563. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06991-8. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38844682 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of guselkumab, an interleukin-23 p19 subunit inhibitor, on enthesitis and dactylitis in patients with moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis: results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase II study.RMD Open. 2020 Jul;6(2):e001217. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001217. RMD Open. 2020. PMID: 32665433 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ixekizumab and complete resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis: integrated analysis of two phase 3 randomized trials in psoriatic arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jan 29;21(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1831-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30696483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of Dactylitis and Enthesitis in Psoriatic Arthritis with Biologic Agents: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis.J Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;47(1):59-65. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180797. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 30824641
-
Biological DMARD efficacy in psoriatic arthritis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis on articular, enthesitis, dactylitis, skin and functional outcomes.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020 May-Jun;38(3):508-515. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31969228
References
-
- Coates LC, Soriano ER, Corp N, Bertheussen H, Callis Duffin K, Campanholo CB, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(12):734. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00861-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

