Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway and daytime dysfunction in women with HIV
- PMID: 38472641
- PMCID: PMC11531856
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-024-01195-x
Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway and daytime dysfunction in women with HIV
Abstract
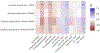
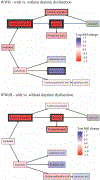
Sleep disturbances are prevalent in women with HIV (WWH). Tryptophan-kynurenine (T-K) pathway metabolites are associated with alterations in actigraphy derived sleep measures in WWH, although may not always correlate with functional impairment. We investigated the relationship between T-K pathway metabolites and self-reported daytime dysfunction in WWH and women without HIV (WWoH). 141 WWH on stable antiretroviral therapy and 140 demographically similar WWoH enrolled in the IDOze Study had targeted plasma T-K metabolites measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. We utilized the daytime dysfunction component of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) to assess functional impairment across HIV-serostatus. Lower levels of 5-hydroxytryptophan and serotonin were associated with greater daytime dysfunction in all women. In WWH, daytime dysfunction was associated with increased kynurenic acid (R = 0.26, p < 0.05), and kynurenic acid-tryptophan (KA-T) ratio (R = 0.28, p < 0.01). WWH with daytime dysfunction had a 0.7 log fold increase in kynurenic acid compared to WWH without daytime dysfunction. Kynurenic acid levels and the KA-T ratio were associated with daytime dysfunction in WWH but not in WWoH. Longitudinal studies are needed to establish a causal relationship and directionality between T-K metabolic changes and sleep impairment in WWH.
Keywords: HIV infection; Kynurenine; Metabolomics; Sleep; Tryptophan; Women.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to The Journal of NeuroVirology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway Activation and Cognition in Virally Suppressed Women With HIV.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024 Aug 15;96(5):494-500. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003454. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38985447 Free PMC article.
-
The IDOze Study: The Link Between Sleep Disruption and Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway Activation in Women With Human Immunodeficiency Virus.J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 17;226(8):1451-1460. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac287. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35801535 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma kynurenine pathway metabolites in association with diabetes: A cross-sectional study.Clin Nutr. 2025 Aug;51:342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2025.07.003. Epub 2025 Jul 7. Clin Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40652781
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The role of tryptophan and its derivatives in musculoskeletal pains: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Oral Rehabil. 2024 Sep;51(9):1898-1910. doi: 10.1111/joor.13758. Epub 2024 May 27. J Oral Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38803211
References
-
- Wu J, Wu H, Lu C, Guo L, Li P. Self-reported sleep disturbances in HIV-infected people: a meta-analysis of prevalence and moderators. Sleep Medicine. 2015; 16(8):901–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 MH075673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL146202/Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS)
- JHU CAHN; P30 MH075673/JHU Center for the Advancement of HIV Neurotherapeutics
- R01 HL142116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL146245/Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS)
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL142116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL146204/Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS)
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

