Temporal Profile of the Microbial Community and Volatile Compounds in the Third-Round Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor baijiu in the Beijing Region
- PMID: 38472783
- PMCID: PMC10931104
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13050670
Temporal Profile of the Microbial Community and Volatile Compounds in the Third-Round Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor baijiu in the Beijing Region
Abstract
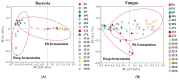
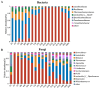
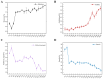
Sauce-flavor baijiu produced in the Beijing and Guizhou regions has regional characteristic flavors, but the differences in flavor compounds and reasons for their formation remain unclear. The sauce-flavor baijiu brewing process involves several rounds of fermentation. In this study, we investigated the temporal distribution of microbial communities and flavor substances during the third round of sauce-flavor baijiu fermentation in the Beijing region, and we then compared and analyzed the differences of flavor substances and microorganisms in the fermented grains of sauce-flavor baijiu in the Beijing and Guizhou regions. It was found that 10 bacterial genera and 10 fungal genera were dominant in the fermented grains. The acidity of the fermented grains had a significant driving effect on the microbial community succession. A total of 81 volatile compounds were identified and quantified in the fermented grains, of which esters and alcohols were relatively abundant. The differences in 30 microbial community compositions and their resulting differences in terms of the fermentation parameters of fermented grains are responsible for the differences in the profiles of flavor compounds between sauce-flavor baijiu produced in the Beijing and Guizhou regions.
Keywords: changes in flavor compounds; microbial community succession; regional flavor characteristics; sauce-flavor baijiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of Environmental Microorganisms on Fermentation Microbial Community of Sauce-Flavor baijiu.Foods. 2022 Dec 20;12(1):10. doi: 10.3390/foods12010010. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36613226 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the correlation between microbial communities with physicochemical properties and flavor substances in the Xiasha round of cave-brewed sauce-flavor Baijiu.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 1;14:1124817. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1124817. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36937267 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact mechanisms on different mechanized airing approaches during second round heap fermentation of sauce-flavor Baijiu: From physicochemical parameters, microbial diversity to volatile flavor compounds.Food Res Int. 2025 Jan;199:115359. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.115359. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 39658161
-
Unraveling the regional environmental ecology dominated baijiu fermentation microbial community succession and associated unique flavor.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1487359. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1487359. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39545237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress on Flavor Compounds and Microorganisms of Maotai Flavor Baijiu.J Food Sci. 2019 Jan;84(1):6-18. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14409. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Food Sci. 2019. PMID: 30548499 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of the improved application of Bacillus halotolerans on the microbial community and volatile components of high-temperature daqu.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1626160. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1626160. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40657499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun J.Y., Zhao D.R., Zhang F.G., Sun B.G., Zheng F.P., Huang M.Q., Li H.H. Joint direct injection and GC-MS chemometric approach for chemical profile and sulfur compounds of sesame-flavor Chinese Baijiu (Chinese liquor) Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018;244:145–160. doi: 10.1007/s00217-017-2938-7. - DOI
-
- Wu Y.L., Hao F., Lv X.B., Chen B., Yang Y.B., Zeng X.L., Wang L. Diversity of lactic acid bacteria in Moutai-flavor liquor fermentation process. Food Biotechnol. 2020;34:212–227. doi: 10.1080/08905436.2020.1789475. - DOI
-
- Xu Y., Zhao J., Huang H., Guo X., Li X., Zou W., Huang M. Biodegradation of phthalate esters by Pantoea dispersa BJQ0007 isolated from Baijiu. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022;105:104201. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104201. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

