Novel Electromagnetic Heat Hydrodistillation for Extraction of Essential Oil from Tangerine Peel
- PMID: 38472790
- PMCID: PMC10930592
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13050677
Novel Electromagnetic Heat Hydrodistillation for Extraction of Essential Oil from Tangerine Peel
Abstract
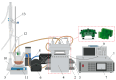
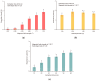
A novel electromagnetic heat method is presented for green extraction of natural compounds from peel residue. In the processing cavity obtained through 3D printing, a core made of amorphous alloy was applied to strengthen the magnetic flux. During the process, an induced electric field was produced in the extract medium owing to an oscillating magnetic field at 50 kHz rather than a pair of electrodes; thus, electrochemical reactions could be avoided. A thermal effect and temperature rise were observed under the field, and essential oil was obtained via this electromagnetic heat hydrodistillation. In addition, the numerical relationships between magnetic field, induced electric field (IEF), induced current density, and temperature profile were elaborated; they were positively correlated with the extraction yield of essential oils. It was found that the waveforms of the magnetic field, induced electric field, and excitation voltage were not consistent. Using a higher magnetic field resulted in high current densities and terminal temperatures in the extracts, as well as higher essential oil yields. When the magnetic field strength was 1.39 T and the extraction time was 60 min, the maximum yield of essential oil reached 1.88%. Meanwhile, conventional hydrodistillation and ohmic heating hydrodistillation were conducted for the comparison; all treatments had no significant impact on the densities. In addition, the essential oil extracted by electromagnetic heat had the lowest acid value and highest saponification value. The proportion of monoterpenoids and oxygen-containing compounds of essential oil extracted by this proposed method was higher than the other two methods. In the end, the development of this electromagnetic heat originating from magnetic energy has the potential to recover high-value compounds from biomass waste.
Keywords: electromagnetic heat; essential oil extraction; oscillating magnetic field; physicochemical properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Physicochemical characterization of pectin extracted from mandarin peels using novel electromagnetic heat.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Mar;262(Pt 2):130212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130212. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38365142
-
Sono hydrodistillation for isolation of citronella oil: A symbiotic effect of sonication and hydrodistillation towards energy efficiency and environment friendliness.Ultrason Sonochem. 2018 Dec;49:145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.07.038. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018. PMID: 30097258
-
Comparison of heat and mass transfer of different microwave-assisted extraction methods of essential oil from Citrus limon (Lisbon variety) peel.Food Sci Nutr. 2015 May 5;3(6):506-18. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.240. eCollection 2015 Nov. Food Sci Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26788292 Free PMC article.
-
Ohmic heating as a promising technique for extraction of herbal essential oils: Understanding mechanisms, recent findings, and associated challenges.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2020;91:227-273. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2020. PMID: 32035597 Review.
-
A step closer to circular bioeconomy for citrus peel waste: A review of yields and technologies for sustainable management of essential oils.J Environ Manage. 2021 Feb 15;280:111832. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111832. Epub 2020 Dec 23. J Environ Manage. 2021. PMID: 33360259 Review.
Cited by
-
New Strategies for the Extraction of Antioxidants from Fruits and Their By-Products: A Systematic Review.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;14(5):755. doi: 10.3390/plants14050755. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40094704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tomato Disease Combat and Yield Optimization Using Selenium Nanoparticles: A Sustainable Nano-Agriculture Approach.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 27;13(7):e70386. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70386. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40585496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farhat A., Fabiano-Tixier A.S., El Maataoui M., Maingonnat J.F., Romdhane M., Chemat F. Microwave steam diffusion for extraction of essential oil from orange peel: Kinetic data, extract’s global yield and mechanism. Food Chem. 2011;125:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.110. - DOI
-
- Satari B., Karimi K. Citrus processing wastes: Environmental impacts, recent advances, and future perspectives in total valorization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018;129:153–167. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.032. - DOI
-
- Prommaban A., Chaiyana W. Microemulsion of essential oils from citrus peels and leaves with anti-aging, whitening, and irritation reducing capacity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022;69:103188. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103188. - DOI
-
- Asikin Y., Shimizu K., Iwasaki H., Oku H., Wada K. Stress amelioration and anti-inflammatory potential of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) essential oil, limonene, and γ-terpinene. J. Food Drug Anal. 2022;30:454–465. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3414. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

