A Highly Sensitive XNA-Based RT-qPCR Assay for the Identification of ALK, RET, and ROS1 Fusions in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 38472960
- PMCID: PMC10930897
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14050488
A Highly Sensitive XNA-Based RT-qPCR Assay for the Identification of ALK, RET, and ROS1 Fusions in Lung Cancer
Abstract
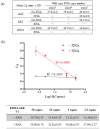
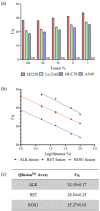
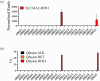
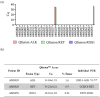
Lung cancer is often triggered by genetic alterations that result in the expression of oncogenic tyrosine kinases. Specifically, ALK, RET, and ROS1 chimeric receptor tyrosine kinases are observed in approximately 5-7%, 1-2%, and 1-2% of NSCLC patients, respectively. The presence of these fusion genes determines the response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Thus, accurate detection of these gene fusions is essential in cancer research and precision oncology. To address this need, we have developed a multiplexed RT-qPCR assay using xeno nucleic acid (XNA) molecular clamping technology to detect lung cancer fusions. This assay can quantitatively detect thirteen ALK, seven ROS1, and seven RET gene fusions in FFPE samples. The sensitivity of the assay was established at a limit of detection of 50 copies of the synthetic template. Our assay has successfully identified all fusion transcripts using 50 ng of RNA from both reference FFPE samples and cell lines. After validation, a total of 77 lung cancer patient FFPE samples were tested, demonstrating the effectiveness of the XNA-based fusion gene assay with clinical samples. Importantly, this assay is adaptable to highly degraded RNA samples with low input amounts. Future steps involve expanding the testing to include a broader range of clinical samples as well as cell-free RNAs to further validate its applicability and reliability.
Keywords: ALK; RET; ROS1; RT-qPCR; XNA; fusion; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
B.L., A.C., A.Y.F., A.Z. and M.Y.S. are employee of DiaCarta Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single-tube multiplexed assay for detecting ALK, ROS1, and RET fusions in lung cancer.J Mol Diagn. 2014 Mar;16(2):229-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.11.007. Epub 2014 Jan 10. J Mol Diagn. 2014. PMID: 24418728
-
Identification of ALK, ROS1, and RET Fusions by a Multiplexed mRNA-Based Assay in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Samples from Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Clin Chem. 2017 Mar;63(3):751-760. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.265314. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28073897
-
Usefulness of an RNA extraction-free test for the multiplexed detection of ALK, ROS1, and RET Gene Fusions in Real Life FFPE Specimens of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(12):1283-1291. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2277367. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023. PMID: 37906110
-
Novel targets in non-small cell lung cancer: ROS1 and RET fusions.Oncologist. 2013;18(7):865-75. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0095. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23814043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other oncogene fusions in lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015 Apr;4(2):156-64. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.11.11. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25870798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

