Critical Roles of the Sphingolipid Metabolic Pathway in Liver Regeneration, Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Therapy
- PMID: 38473211
- PMCID: PMC10931359
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050850
Critical Roles of the Sphingolipid Metabolic Pathway in Liver Regeneration, Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Therapy
Abstract
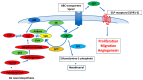
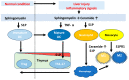
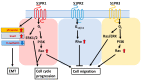
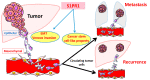
The sphingolipid metabolic pathway, an important signaling pathway, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes including cell proliferation, survival, apoptosis, and immune regulation. The liver has the unique ability to regenerate using bioactive lipid mediators involving multiple sphingolipids, including ceramide and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). Dysregulation of the balance between sphingomyelin, ceramide, and S1P has been implicated in the regulation of liver regeneration and diseases, including liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding and modulating this balance may have therapeutic implications for tumor proliferation, progression, and metastasis in HCC. For cancer therapy, several inhibitors and activators of sphingolipid signaling, including ABC294640, SKI-II, and FTY720, have been discussed. Here, we elucidate the critical roles of the sphingolipid pathway in the regulation of liver regeneration, fibrosis, and HCC. Regulation of sphingolipids and their corresponding enzymes may considerably influence new insights into therapies for various liver disorders and diseases.
Keywords: HCC; liver fibrosis; liver regeneration; the sphingolipid metabolic pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolic enzymes leads to high levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate and ceramide in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Res. 2021 May;51(5):614-626. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13625. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Hepatol Res. 2021. PMID: 33586816
-
Sphingolipids in liver injury, repair and regeneration.Biol Chem. 2015 Jun;396(6-7):633-43. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0296. Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25781682 Review.
-
Neuroprotective role of sphingolipid rheostat in excitotoxic retinal ganglion cell death.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Jul;208:108623. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108623. Epub 2021 May 19. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34022173
-
Sorafenib Treatment and Modulation of the Sphingolipid Pathway Affect Proliferation and Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 31;21(7):2409. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072409. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32244391 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Sphingolipid Metabolism as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(9):2183. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092183. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics insights into the protective molecular mechanism of Vaccinium myrtillus against oxidative stress in intestinal cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8643. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93722-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082563 Free PMC article.
-
Streptozotocin and L-Buthionine-Sulfoximine Decrease Neuron Membrane Lipid Packing and Alter Insulin Signaling.Neurotox Res. 2025 May 29;43(3):24. doi: 10.1007/s12640-025-00749-z. Neurotox Res. 2025. PMID: 40439741
-
The role of ACER2 in intestinal sphingolipid metabolism and gastrointestinal cancers.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 22;15:1511283. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1511283. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39650647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amelioration of Fibrosis via S1P Inhibition Is Regulated by Inactivation of TGF-β and SPL Pathways in the Human Cornea.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6560. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126560. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928268 Free PMC article.
-
SMPD3 as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Genomics. 2025 Mar 11;2025:5443244. doi: 10.1155/ijog/5443244. eCollection 2025. Int J Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40226357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nojima H., Kuboki S., Shinoda K., Shimizu H., Ohtsuka M., Kato A., Yoshitomi H., Furukawa K., Takayashiki T., Miyazaki M. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma inhibits tumor growth by negatively regulating nuclear factor-κB activation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2016;23:574–584. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.378. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

