Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38473213
- PMCID: PMC10930866
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050851
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Extracranial Oligometastatic Disease from Head and Neck Primary Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is increasingly used to treat disease in the oligometastatic (OM) setting due to mounting evidence demonstrating its efficacy and safety. Given the low population representation in prospective studies, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes of HNC patients with extracranial OM disease treated with SBRT.
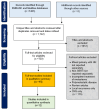
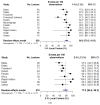
Methods: A systematic review was conducted with Cochrane, Medline, and Embase databases queried from inception to August 2022 for studies with extracranial OM HNC treated with stereotactic radiotherapy. Polymetastatic patients (>five lesions), mixed-primary cohorts failing to report HNC separately, lack of treatment to all lesions, nonquantitative endpoints, and other definitive treatments (surgery, conventional radiotherapy, and radioablation) were excluded. The meta-analysis examined the pooled effects of 12- and 24-month local control (LC) per lesion, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Weighted random-effects were assessed using the DerSimonian and Laird method, with heterogeneity evaluated using the I2 statistic and Cochran Qtest. Forest plots were generated for each endpoint.
Results: Fifteen studies met the inclusion criteria (639 patients, 831 lesions), with twelve eligible for quantitative synthesis with common endpoints and sufficient reporting. Fourteen studies were retrospective, with a single prospective trial. Studies were small, with a median of 32 patients (range: 6-81) and 63 lesions (range: 6-126). The OM definition varied, with a maximum of two to five metastases, mixed synchronous and metachronous lesions, and a few studies including oligoprogressive lesions. The most common site of metastasis was the lung. Radiation was delivered in 1-10 fractions (20-70 Gy). The one-year LC (LC1), reported in 12 studies, was 86.9% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 79.3-91.9%). LC2 was 77.9% (95% CI: 66.4-86.3%), with heterogeneity across studies. PFS was reported in five studies, with a PFS1 of 43.0% (95% CI: 35.0-51.4%) and PFS2 of 23.9% (95% CI: 17.8-31.2%), with homogeneity across studies. OS was analyzed in nine studies, demonstrating an OS1 of 80.1% (95% CI: 74.2-85.0%) and OS2 of 60.7% (95% CI: 51.3-69.4%). Treatment was well tolerated with no reported grade 4 or 5 toxicities. Grade 3 toxicity rates were uniformly below 5% when reported.
Conclusions: SBRT offers excellent LC and promising OS, with acceptable toxicities in OM HNC. Durable PFS remains rare, highlighting the need for effective local or systemic therapies in this population. Further investigations on concurrent and adjuvant therapies are warranted.
Keywords: HNSCC; SABR; SBRT; oligometastases; oligoprogression.
Conflict of interest statement
A.V.L. received honoraria and serves on an advisory board for Astra Zeneca, which is unrelated to the present work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment Outcomes of Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy on Extra-cranial Oligometastatic and Oligoprogressive Breast Cancer: Mature Results from a Single Institution Experience.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024 Jun;36(6):362-369. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.03.012. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024. PMID: 38575431
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for distant metastases to the head and neck.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Mar 15;32(4):230. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08419-0. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38488881
-
Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma (SABR ORCA): a meta-analysis of 28 studies.Eur Urol Oncol. 2019 Sep;2(5):515-523. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2019.05.007. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31302061
-
Extracranial Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic or Oligoprogressive Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 26;10:987. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00987. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32676455 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Oligorecurrent/Oligoprogressive Mediastinal and Hilar Lymph Node Metastasis: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 28;14(11):2680. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112680. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying optimal candidates for primary tumor surgery in patients with metastatic head and neck cancer.Front Surg. 2024 Apr 10;11:1394809. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1394809. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38665696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis S.L., Porceddu S., Nakamura N., Palma D.A., Lo S.S., Hoskin P., Moghanaki D., Chmura S.J., Salama J.K. Definitive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Extracranial Oligometastases: An International Survey of >1000 Radiation Oncologists. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;40:418–422. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000169. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olson R., Jiang W., Liu M., Bergman A., Schellenberg D., Mou B., Alexander A., Carolan H., Hsu F., Miller S., et al. Treatment With Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Up to 5 Oligometastases in Patients With Cancer: Primary Toxic Effect Results of the Nonrandomized Phase 2 SABR-5 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022 doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qu X.M., Chen Y., Zaric G.S., Senan S., Olson R.A., Harrow S., John-Baptiste A., Gaede S., Mulroy L.A., Schellenberg D., et al. Is SABR Cost-Effective in Oligometastatic Cancer? An Economic Analysis of the SABR-COMET Randomized Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021;109:1176–1184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barry A.S., Helou J., Bezjak A., Wong R., Dawson L.A., Ringash J., Fazelzad R., Liu Z., Olson R., Palma D., et al. Health related quality of life outcomes following stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with oligo-metastatic disease: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2022;173:163–169. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.05.033. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous