Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38473311
- PMCID: PMC10931025
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050949
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
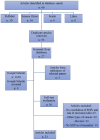
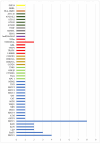
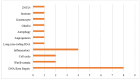
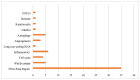
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most common type of genetic variation found in an individual's DNA sequences. SNPs can occur in both coding and non-coding regions of the genome and can affect gene expression, protein function, and disease susceptibility. In this systematic review, we evaluate the potential of SNPs as biomarkers in the assessment of oral mucositis (OM) severity in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients treated with concomitant chemoradiation (CRT). The study selection process involved screening 66 articles from different platforms, and after removing duplicates and excluding articles that did not meet the eligibility criteria, 23 articles were included for full-text evaluation. Among them, genes from several pathways were analyzed. The DNA damage repair pathways had the highest number of genes studied. The most frequently analyzed gene was XRCC1. The proinflammatory cytokine pathways evaluated were TNF, with three articles, and NF-κB, with one article. Most included studies showed a potential association between certain SNPs and high-grade mucositis. We conclude that SNPs can be used as possible biomarkers for the assessment of OM intensity in HNC patients, and further research is needed to explore the potential of SNPs in personalized medicine for HNC treatment.
Keywords: SNPs; chemoradiotherapy; head and neck cancer; mucositis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wolf G., Fisher S., Hong W., Hilman R., Spaulding M., Laramore G. Induction chemotherapy plus radiation compared with surgery plus radiation in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;324:1685–1690. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

