miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment
- PMID: 38473318
- PMCID: PMC10931375
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050957
miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment
Abstract
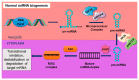
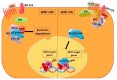
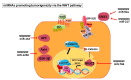
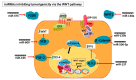
Carcinogenesis is a complex process characterized by intricate changes in organ histology, biochemistry, epigenetics, and genetics. Within this intricate landscape, cancer stem cells (CSCs) have emerged as distinct cell types possessing unique attributes that significantly contribute to the pathogenesis of cancer. The WNT signaling pathway plays a critical role in maintaining somatic stem cell pluripotency. However, in cancer, overexpression of WNT mediators enhances the activity of β-catenin, resulting in phenomena such as recurrence and unfavorable survival outcomes. Notably, CSCs exhibit heightened WNT signaling compared to bulk cancer cells, providing intriguing insights into their functional characteristics. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as post-transcriptional gene expression regulators, modulate various physiological processes in numerous diseases including cancer. Upregulation or downregulation of miRNAs can affect the production of pro-oncogenic or anti-oncogenic proteins, influencing cellular processes that maintain tissue homeostasis and promote either apoptosis or differentiation, even in cancer cells. In order to understand the dysregulation of miRNAs, it is essential to examine miRNA biogenesis and any possible alterations at each step. The potential of a miRNA as a biomarker in prognosis, diagnosis, and detection is being assessed using technologies such as next-generation sequencing. Extensive research has explored miRNA expression profiles in cancer, leading to their utilization as diagnostic tools and the development of personalized and targeted cancer therapies. This review delves into the role of miRNAs in carcinogenesis in relation to the WNT signaling pathway along with their potential as druggable compounds.
Keywords: WNT signaling pathway; cancer stem cells; miRNA therapeutics; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Sudha Warrier was employed by the company Cuor Stem Cellutions Pvt Ltd., Manipal Institute of Regenerative Medicine, Manipal Academy of Higher 14 Education (MAHE). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The dual roles of circRNAs in Wnt/β-Catenin signaling and cancer progression.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Mar;255:155132. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155132. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38335783 Review.
-
miR-19 targeting of GSK3β mediates sulforaphane suppression of lung cancer stem cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 Jun;44:80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Apr 5. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28431267
-
Wnt-signalling pathways and microRNAs network in carcinogenesis: experimental and bioinformatics approaches.Mol Cancer. 2016 Sep 2;15(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0541-3. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27590724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of miR-501-5p activates the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and enhances stem cell-like phenotype in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 15;35(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0432-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27846906 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA and cancer; computational and experimental approaches.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(5):429. doi: 10.2174/138920101505140828161335. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25189575
Cited by
-
Comprehension of PTEN-Regulated MicroRNA Profiling in Oral Premalignant Lesions: A Critical Link to Early Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):e82343. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82343. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40385769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathway mechanisms of circadian clock gene Bmal1 regulating bone and cartilage metabolism: a review.Bone Res. 2025 Jan 27;13(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00403-6. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 39870641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting drug resistance in breast cancer: the potential of miRNA and nanotechnology-driven delivery systems.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Nov 12;6(24):6079-6095. doi: 10.1039/d4na00660g. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39569336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

