Tumor Predisposing Post-Zygotic Chromosomal Alterations in Bladder Cancer-Insights from Histologically Normal Urothelium
- PMID: 38473323
- PMCID: PMC10930680
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050961
Tumor Predisposing Post-Zygotic Chromosomal Alterations in Bladder Cancer-Insights from Histologically Normal Urothelium
Abstract
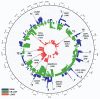
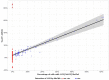
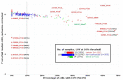
Bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA) is the 10th most common cancer with a low survival rate and strong male bias. We studied the field cancerization in BLCA using multi-sample- and multi-tissue-per-patient protocol for sensitive detection of autosomal post-zygotic chromosomal alterations and loss of chromosome Y (LOY). We analysed 277 samples of histologically normal urothelium, 145 tumors and 63 blood samples from 52 males and 15 females, using the in-house adapted Mosaic Chromosomal Alterations (MoChA) pipeline. This approach allows identification of the early aberrations in urothelium from BLCA patients. Overall, 45% of patients exhibited at least one alteration in at least one normal urothelium sample. Recurrence analysis resulted in 16 hotspots composed of either gains and copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity (CN-LOH) or deletions and CN-LOH, encompassing well-known and new BLCA cancer driver genes. Conservative assessment of LOY showed 29%, 27% and 18% of LOY-cells in tumors, blood and normal urothelium, respectively. We provide a proof of principle that our approach can characterize the earliest alterations preconditioning normal urothelium to BLCA development. Frequent LOY in blood and urothelium-derived tissues suggest its involvement in BLCA.
Keywords: bladder carcinoma (BLCA); chromosomal copy number alterations; copy neutral loss of heterozygosity (CN-LOH); cystectomy; loss of heterozygosity (LOH); mosaic loss of chromosome Y (LOY); normal urothelium; post-zygotic mutations; transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.D. is cofounder and shareholder in Cray Innovation AB. The remaining authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures

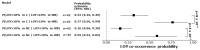
Similar articles
-
Deletions of chromosomes 9 and 8p in histologically normal urothelium of patients with bladder cancer.Eur Urol. 2005 Jan;47(1):58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2004.07.012. Eur Urol. 2005. PMID: 15582250
-
Loss of heterozygosity at 9q32-33 (DBC1 locus) in primary non-invasive papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential and low-grade urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and their associated normal urothelium.J Pathol. 2008 Jul;215(3):263-72. doi: 10.1002/path.2353. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18452128
-
Analysis of genetic alterations in normal bladder urothelium.Urology. 2003 Dec;62(6):1134-8. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(03)00692-7. Urology. 2003. PMID: 14665377
-
[Molecular changes in development and progression of urothelial carcinoma].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2003;87:172-84. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2003. PMID: 16888910 Review. German.
-
The urothelial gene regulatory network: understanding biology to improve bladder cancer management.Oncogene. 2024 Jan;43(1):1-21. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02876-3. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 37996699 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of the Y Chromosome: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms, Age Inference, and Implications for Men's Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 11;25(8):4230. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084230. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of mosaic loss of the Y chromosome (mLOY) in men of advanced age.Biogerontology. 2024 Nov;25(6):943-955. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10133-7. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 39223433 Review.
-
The effects of loss of Y chromosome on male health.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 May;26(5):320-335. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00805-y. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39743536 Review.
-
A complex systems approach to mosaic loss of the Y chromosome.Geroscience. 2025 Feb;47(1):631-651. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01468-7. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39680277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Facchini G., Cavaliere C., Romis L., Mordente S., Facchini S., Iovane G., Capasso M., D’Errico D., Liguori C., Formato R., et al. Advanced/metastatic bladder cancer: Current status and future directions. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;24:11536–11552. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202011_23795. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.A., Naghavi M. Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health. 2021;6:e004128. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

