Forchlorfenuron-Induced Mitochondrial Respiration Inhibition and Metabolic Shifts in Endometrial Cancer
- PMID: 38473335
- PMCID: PMC10931130
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16050976
Forchlorfenuron-Induced Mitochondrial Respiration Inhibition and Metabolic Shifts in Endometrial Cancer
Abstract
Forchlorfenuron (FCF) is a widely used plant cytokinin that enhances fruit quality and size in agriculture. It also serves as a crucial pharmacological tool for the inhibition of septins. However, the precise target of FCF has not yet been fully determined. This study reveals a novel target of FCF and elucidates its downstream signaling events. FCF significantly impairs mitochondrial respiration and mediates metabolic shift toward glycolysis, thus making cells more vulnerable to glycolysis inhibition. Interestingly, FCF's impact on mitochondrial function persists, even in cells lacking septins. Furthermore, the impaired mitochondrial function leads to the degradation of HIF-1α, facilitated by increased cellular oxygen. FCF also induces AMPK activation, suppresses Erk1/2 phosphorylation, and reduces the expression of HER2, β-catenin, and PD-L1. Endometrial cancer is characterized by metabolic disorders such as diabetes and aberrant HER2/Ras-Erk1/2/β-catenin signaling. Thus, FCF may hold promise as a potential therapeutic in endometrial cancer.
Keywords: AMPK; endometrial cancer; forchlorfenuron; mitochondrial respiration; septins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
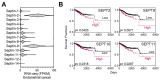


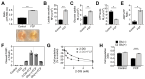




Similar articles
-
Forchlorfenuron disrupts SEPT9_i1 filaments and inhibits HIF-1.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 19;8(8):e73179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073179. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977378 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Potent Forchlorfenuron Analogs and Their Cytotoxic Effect in Cancer Cell Lines.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 24;10(1):3241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59824-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32094384 Free PMC article.
-
Off-target effects of the septin drug forchlorfenuron on nonplant eukaryotes.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Nov;13(11):1411-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.00191-14. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 25217460 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic evolutionary roots of the macrophage immune response in amoeba-bacteria interactions: The conserved role of hypoxia-induced Factor and AMP kinase.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 Aug 10;68(3):457-476. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5683. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 34374500 Review.
-
The Key Role of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancers under Normoxic Conditions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;13(21):5557. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215557. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shantz E.M., Steward F.C. The Identification of Compound A from Coconut Milk as 1,3-Diphenylurea1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955;77:6351–6353. doi: 10.1021/ja01628a079. - DOI
-
- Bruce M.I., Zwar J.A., Kefford N.P. Chemical structure and plant kinin activity— the activity of urea and thiourea derivatives. Life Sci. 1965;4:461–466. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90094-9. - DOI
-
- Takahashi S., Shudo K., Okamoto T.K., Yamada K., Isogai Y. Cytokinin activity of N-phenyl-N2-(4-pyridyl)urea derivatives. Phytochemistry. 1978;17:1201–1207. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)94556-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

