Automatic 3D Augmented-Reality Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy Using Machine Learning: Our Pioneer Experience
- PMID: 38473404
- PMCID: PMC10931272
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16051047
Automatic 3D Augmented-Reality Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy Using Machine Learning: Our Pioneer Experience
Abstract
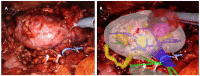
The aim of "Precision Surgery" is to reduce the impact of surgeries on patients' global health. In this context, over the last years, the use of three-dimensional virtual models (3DVMs) of organs has allowed for intraoperative guidance, showing hidden anatomical targets, thus limiting healthy-tissue dissections and subsequent damage during an operation. In order to provide an automatic 3DVM overlapping in the surgical field, we developed and tested a new software, called "ikidney", based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). From January 2022 to April 2023, patients affected by organ-confined renal masses amenable to RAPN were enrolled. A bioengineer, a software developer, and a surgeon collaborated to create hyper-accurate 3D models for automatic 3D AR-guided RAPN, using CNNs. For each patient, demographic and clinical data were collected. A total of 13 patients were included in the present study. The average anchoring time was 11 (6-13) s. Unintended 3D-model automatic co-registration temporary failures happened in a static setting in one patient, while this happened in one patient in a dynamic setting. There was one failure; in this single case, an ultrasound drop-in probe was used to detect the neoplasm, and the surgery was performed under ultrasound guidance instead of AR guidance. No major intraoperative nor postoperative complications (i.e., Clavien Dindo > 2) were recorded. The employment of AI has unveiled several new scenarios in clinical practice, thanks to its ability to perform specific tasks autonomously. We employed CNNs for an automatic 3DVM overlapping during RAPN, thus improving the accuracy of the superimposition process.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; kidney cancer; nephron-sparing surgery; partial nephrectomy; renal cell carcinoma; robotic surgery; three-dimensional imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Minervini A., Campi R., Lane B.R., De Cobelli O., Sanguedolce F., Hatzichristodoulou G., Antonelli A., Noyes S., Mari A., Rodriguez-Faba O., et al. Impact of Resection Technique on Perioperative Outcomes and Surgical Margins after Partial Nephrectomy for Localized Renal Masses: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Urol. 2020;203:496–504. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000591. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghazi A., Melnyk R., Hung A.J., Collins J., Ertefaie A., Saba P., Gurung P., Frye T., Rashid H., Wu G., et al. Multi-Institutional Validation of a Perfused Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy Procedural Simulation Platform Utilizing Clinically Relevant Objective Metrics of Simulators (CROMS) BJU Int. 2021;127:645–653. doi: 10.1111/bju.15246. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amparore D., Pecoraro A., Checcucci E., DE Cillis S., Piramide F., Volpi G., Piana A., Verri P., Granato S., Sica M., et al. 3D Imaging Technologies in Minimally Invasive Kidney and Prostate Cancer Surgery: Which Is the Urologists’ Perception? Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2022;74:178–185. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.21.04131-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

