A 30-Year Review on Nanocomposites: Comprehensive Bibliometric Insights into Microstructural, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties Assisted by Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 38473560
- PMCID: PMC10934506
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17051088
A 30-Year Review on Nanocomposites: Comprehensive Bibliometric Insights into Microstructural, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties Assisted by Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
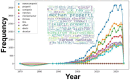
From 1990 to 2024, this study presents a groundbreaking bibliometric and sentiment analysis of nanocomposite literature, distinguishing itself from existing reviews through its unique computational methodology. Developed by our research group, this novel approach systematically investigates the evolution of nanocomposites, focusing on microstructural characterization, electrical properties, and mechanical behaviors. By deploying advanced Boolean search strategies within the Scopus database, we achieve a meticulous extraction and in-depth exploration of thematic content, a methodological advancement in the field. Our analysis uniquely identifies critical trends and insights concerning nanocomposite microstructure, electrical attributes, and mechanical performance. The paper goes beyond traditional textual analytics and bibliometric evaluation, offering new interpretations of data and highlighting significant collaborative efforts and influential studies within the nanocomposite domain. Our findings uncover the evolution of research language, thematic shifts, and global contributions, providing a distinct and comprehensive view of the dynamic evolution of nanocomposite research. A critical component of this study is the "State-of-the-Art and Gaps Extracted from Results and Discussions" section, which delves into the latest advancements in nanocomposite research. This section details various nanocomposite types and their properties and introduces novel interpretations of their applications, especially in nanocomposite films. By tracing historical progress and identifying emerging trends, this analysis emphasizes the significance of collaboration and influential studies in molding the field. Moreover, the "Literature Review Guided by Artificial Intelligence" section showcases an innovative AI-guided approach to nanocomposite research, a first in this domain. Focusing on articles from 2023, selected based on citation frequency, this method offers a new perspective on the interplay between nanocomposites and their electrical properties. It highlights the composition, structure, and functionality of various systems, integrating recent findings for a comprehensive overview of current knowledge. The sentiment analysis, with an average score of 0.638771, reflects a positive trend in academic discourse and an increasing recognition of the potential of nanocomposites. Our bibliometric analysis, another methodological novelty, maps the intellectual domain, emphasizing pivotal research themes and the influence of crosslinking time on nanocomposite attributes. While acknowledging its limitations, this study exemplifies the indispensable role of our innovative computational tools in synthesizing and understanding the extensive body of nanocomposite literature. This work not only elucidates prevailing trends but also contributes a unique perspective and novel insights, enhancing our understanding of the nanocomposite research field.
Keywords: Boolean search; Scopus database; bibliometric analysis; computational methodologies; crosslinking time; microstructural characterization; nanocomposites; sentiment analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
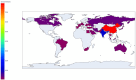
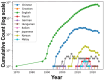
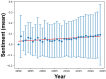
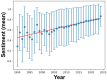




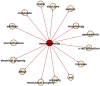

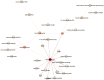
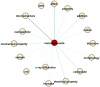
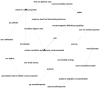


Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Machine learning and artificial intelligence in type 2 diabetes prediction: a comprehensive 33-year bibliometric and literature analysis.Front Digit Health. 2025 Mar 27;7:1557467. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1557467. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40212895 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocomposites for Multifunctional Sensors: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Exploration.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Dec 29;15(1):34. doi: 10.3390/nano15010034. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39791793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Intellectual Landscape of Nanovaccines: A Bibliometric Perspective on Scientific Progress and Future Directions.Cureus. 2024 May 12;16(5):e60131. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60131. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38868255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control charts in healthcare quality monitoring: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis.Int J Qual Health Care. 2024 Jul 19;36(3):mzae060. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzae060. Int J Qual Health Care. 2024. PMID: 39018022
Cited by
-
Anisotropic piezoresistive response of 3D-printed pressure sensor based on ABS/MWCNT nanocomposite.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76028-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omanović-Mikličanin E., Badnjević A., Kazlagić A., Hajlovac M. Nanocomposites: A Brief Review. Health Technol. 2020;10:51–59. doi: 10.1007/s12553-019-00380-x. - DOI
-
- Rajani A., Chauhan P., Dave P.Y. Nanocomposites: A New Tendency of Structure in Nanotechnology and Material Science. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2021;7:937–941. doi: 10.30799/jnst.315.21070103. - DOI
-
- Dhinakaran V., Sai M.S., Shree M.V. Nanocomposites: Introduction, Structure, Properties and Preparation Methods. In: Singh M., Rai V.K., Rai A., editors. Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes. Volume 2. Bentham Science Publishers; Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: 2022. pp. 1–14.
-
- Fu S.-Y., Mai Y.-W., Du S.-Y., Hui D. Preparation, Properties and Applications of Nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011;42:2091–2092. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.05.001. - DOI
-
- Martínez E.D., Prado A., Gonzalez M., Anguiano S., Tosi L., Salazar Alarcón L., Pastoriza H. Recent Advances on Nanocomposite Resists With Design Functionality for Lithographic Microfabrication. Front. Mater. 2021;8:629792. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2021.629792. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

