Changes in the Expression of Proteins Associated with Neurodegeneration in the Brains of Mice after Infection with Influenza A Virus with Wild Type and Truncated NS1
- PMID: 38473707
- PMCID: PMC10931352
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052460
Changes in the Expression of Proteins Associated with Neurodegeneration in the Brains of Mice after Infection with Influenza A Virus with Wild Type and Truncated NS1
Abstract
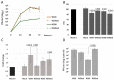
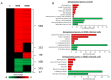
Influenza type A virus (IAV) infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality during influenza epidemics. Recently, a specific link between IAV infection and neurodegenerative disease progression has been established. The non-structural NS1 protein of IAV regulates viral replication during infection and antagonizes host antiviral responses, contributing to influenza virulence. In the present study, we have prepared a mouse lung-to-lung adapted to the NS1-truncated virus (NS80ad). Transcriptome analysis of the gene expression in the lungs revealed that infection with wild-type A/WSN/33 (WSN), NS80, and NS80ad viruses resulted in different regulation of genes involved in signaling pathways associated with the cell proliferation, inflammatory response, and development of neurodegenerative diseases. NS1 protein did not influence the genes involved in the RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway in the brains. Lethal infection with IAVs dysregulated expression of proteins associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases (CX3CL1/Fractalkine, Coagulation factor III, and CD105/Endoglin, CD54/ICAM-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, IGFBP-5, IGFBP-6, chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1), Myeloperoxidase (MPO), Osteopontin (OPN), cystatin C, and LDL R). Transcription of GATA3 mRNA was decreased, and expression of MPO was inhibited in the brain infected with NS80 and NS80ad viruses. In addition, the truncation of NS1 protein led to reduced expression of IGFBP-2, CHI3L1, MPO, and LDL-R proteins in the brains. Our results indicate that the influenza virus influences the expression of proteins involved in brain function, and this might occur mostly through the NS1 protein. These findings suggest that the abovementioned proteins represent a promising target for the development of potentially effective immunotherapy against neurodegeneration.
Keywords: NS1 protein; adaptation; brain; immune response; inflammation; influenza virus; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Differential Modulation of Innate Immune Responses in Human Primary Cells by Influenza A Viruses Carrying Human or Avian Nonstructural Protein 1.J Virol. 2019 Dec 12;94(1):e00999-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00999-19. Print 2019 Dec 12. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31597767 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of PA-X and NS1 Proteins in Replication and Pathogenesis of a Temperature-Sensitive 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza A Virus.J Virol. 2017 Aug 10;91(17):e00720-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00720-17. Print 2017 Sep 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28637750 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Innate Immune Responses by the Influenza A NS1 and PA-X Proteins.Viruses. 2018 Dec 12;10(12):708. doi: 10.3390/v10120708. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30545063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Role for PDZ-Binding Motif of Influenza A Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 in Regulation of Host Susceptibility to Postinfluenza Bacterial Superinfections.Viral Immunol. 2019 Apr;32(3):131-143. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0118. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Viral Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30822217 Free PMC article.
-
Live attenuated influenza A virus vaccines with modified NS1 proteins for veterinary use.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 22;12:954811. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.954811. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35937688 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) of influenza a virus.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2359470. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2359470. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38918890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hosseini S., Wilk E., Michaelsen-Preusse K., Gerhauser I., Baumgärtner W., Geffers R., Schughart K., Korte M. Long-Term Neuroinflammation Induced by Influenza A Virus Infection and the Impact on Hippocampal Neuron Morphology and Function. J. Neurosci. 2018;38:3060–3080. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1740-17.2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

