P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation
- PMID: 38473726
- PMCID: PMC10931347
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052479
P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation
Abstract
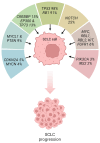
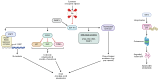
The genes coding for the tumor suppressors p53 and retinoblastoma (Rb) are inactivated in the vast majority of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumors. Data support the notion that these two deleterious genetic events represent the initial steps in the development of SCLC, making them essential for a lung epithelial cell to progress toward the acquisition of a malignant phenotype. With the loss of TP53 and RB1, their broad tumor suppressive functions are eliminated and a normal cell is able to proliferate indefinitely, escape entering into cellular senescence, and evade death, no matter the damage it has experienced. Within this setting, lung epithelial cells accumulate further oncogenic mutations and are well on their way to becoming SCLC cells. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of these genetic lesions and their effects within lung epithelial cells is of paramount importance, in order to tackle this aggressive and deadly lung cancer. The present review summarizes the current knowledge on p53 and Rb aberrations, their biological significance, and their prospective therapeutic potential, highlighting completed and ongoing clinical trials with agents that target downstream pathways.
Keywords: Rb; genetic alterations and aberrations; mutations; p53; small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rb Tumor Suppressor in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Combined Genomic and IHC Analysis with a Description of a Distinct Rb-Proficient Subset.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 1;28(21):4702-4713. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-1115. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35792876 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and genomic comparisons between different histologic components in combined small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2018 Nov;125:282-290. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30429033
-
NOTCH, ASCL1, p53 and RB alterations define an alternative pathway driving neuroendocrine and small cell lung carcinomas.Int J Cancer. 2016 Feb 15;138(4):927-38. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29835. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26340530 Free PMC article.
-
Small cell lung cancer: significance of RB alterations and TTF-1 expression in its carcinogenesis, phenotype, and biology.Endocr Pathol. 2009 Summer;20(2):101-7. doi: 10.1007/s12022-009-9072-4. Endocr Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19390995 Review.
-
Targeted pharmacologic inhibition of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) mediated cell cycle regulation in lung and other RB-Related cancers: A brief review of current status and future prospects.Adv Biol Regul. 2023 May;88:100964. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2023.100964. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Adv Biol Regul. 2023. PMID: 37004354 Review.
Cited by
-
Mixtures of Three Mortaparibs with Enhanced Anticancer, Anti-Migration, and Antistress Activities: Molecular Characterization in p53-Null Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 17;16(12):2239. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122239. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927944 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;17(7):1110. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071110. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Genetic Mutations on the Efficacy of Immunotherapies in Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 7;25(22):11954. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211954. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of the 5th WHO Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Lung Carcinoma in Small Lung Biopsies in a Tertiary Care Center: Is Insecurity of Pathologists for the Accurate Diagnosis Justified?Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;14(18):2090. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14182090. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335769 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring lung cancer microenvironment: pathways and nanoparticle-based therapies.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 11;16(1):159. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01902-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39934547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

