Deep Flow Cytometry Unveils Distinct Immune Cell Subsets in Inducible T Cell Co-Stimulator Ligand (ICOSL)- and ICOS-Knockout Mice during Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 38473756
- PMCID: PMC10932052
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052509
Deep Flow Cytometry Unveils Distinct Immune Cell Subsets in Inducible T Cell Co-Stimulator Ligand (ICOSL)- and ICOS-Knockout Mice during Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
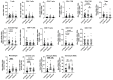
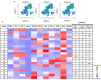
The inducible T cell co-stimulator ligand (ICOSL), expressed by antigen presenting cells, binds to the inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) on activated T cells. Improper function of the ICOS/ICOSL pathway has been implicated in several autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS). Previous studies showed that ICOS-knockout (KO) mice exhibit severe experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of MS, but data on ICOSL deficiency are not available. In our study, we explored the impact of both ICOS and ICOSL deficiencies on MOG35-55 -induced EAE and its associated immune cell dynamics by employing ICOSL-KO and ICOS-KO mice with a C57BL/6J background. During EAE resolution, MOG-driven cytokine levels and the immunophenotype of splenocytes were evaluated by ELISA and multiparametric flow cytometry, respectively. We found that both KO mice exhibited an overlapping and more severe EAE compared to C57BL/6J mice, corroborated by a reduction in memory/regulatory T cell subsets and interleukin (IL-)17 levels. It is noteworthy that an unsupervised analysis showed that ICOSL deficiency modifies the immune response in an original way, by affecting T central and effector memory (TCM, TEM), long-lived CD4+ TEM cells, and macrophages, compared to ICOS-KO and C57BL/6J mice, suggesting a role for other binding partners to ICOSL in EAE development, which deserves further study.
Keywords: ICOSL; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; memory cells; multiple sclerosis; regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Dynamic alteration of CD154/CD40 and its effects on Th1/Th2 polarization in inducible co-stimulator ligand knockout mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Dec 18;47(6):898-904. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 26679647 Chinese.
-
ICOS-Fc as innovative immunomodulatory approach to counteract inflammation and organ injury in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:992614. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.992614. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119089 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Balanced Involvement of the ICOS/ICOSL/Osteopontin Network in Cutaneous Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 19;25(22):12390. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212390. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596455 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of ICOS and ICOS Ligand in Corneal Transplantation and in Maintenance of Immune Privilege.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Dec 1;57(15):6815-6823. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20644. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 28002569
-
The rationale behind targeting the ICOS-ICOS ligand costimulatory pathway in cancer immunotherapy.ESMO Open. 2020 Jan;5(1):e000544. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000544. ESMO Open. 2020. PMID: 32516116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conjunctival MicroRNA Expression Signature in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome Dry Eye: A NanoString-Based Bioinformatic Analysis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Apr 1;66(4):80. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.4.80. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40298889 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

