Multi-Omics Analysis of the Effects of Soil Amendment on Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Photosynthesis under Drip Irrigation with Brackish Water
- PMID: 38473771
- PMCID: PMC10931354
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052521
Multi-Omics Analysis of the Effects of Soil Amendment on Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Photosynthesis under Drip Irrigation with Brackish Water
Abstract
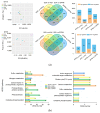
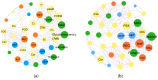
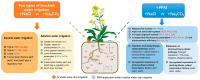
Drip irrigation with brackish water increases the risk of soil salinization while alleviating water shortage in arid areas. In order to alleviate soil salinity stress on crops, polymer soil amendments are increasingly used. But the regulation mechanism of a polymer soil amendment composed of polyacrylamide polyvinyl alcohol, and manganese sulfate (PPM) on rapeseed photosynthesis under drip irrigation with different types of brackish water is still unclear. In this field study, PPM was applied to study the responses of the rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) phenotype, photosynthetic physiology, transcriptomics, and metabolomics at the peak flowering stage under drip irrigation with water containing 6 g·L-1 NaCl (S) and Na2CO3 (A). The results showed that the inhibitory effect of the A treatment on rapeseed photosynthesis was greater than that of the S treatment, which was reflected in the higher Na+ content (73.30%) and lower photosynthetic-fluorescence parameters (6.30-61.54%) and antioxidant enzyme activity (53.13-77.10%) of the A-treated plants. The application of PPM increased the biomass (63.03-75.91%), photosynthetic parameters (10.55-34.06%), chlorophyll fluorescence parameters (33.83-62.52%), leaf pigment content (10.30-187.73%), and antioxidant enzyme activity (28.37-198.57%) under S and A treatments. However, the difference is that under the S treatment, PPM regulated the sulfur metabolism, carbon fixation and carbon metabolism pathways in rapeseed leaves. And it also regulated the photosynthesis-, oxidative phosphorylation-, and TCA cycle-related metabolic pathways in rapeseed leaves under A treatment. This study will provide new insights for the application of polymer materials to tackle the salinity stress on crops caused by drip irrigation with brackish water, and solve the difficulty in brackish water utilization.
Keywords: abiotic stresses; brackish water; energy metabolism; metabolic pathways; multi-omics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Leogrande R., Vitti C., Lopedota O., Ventrella D., Montemurro F. Effects of irrigation volume and saline water on maize yield and soil in Southern Italy. Irrig. Drain. 2016;65:243–253. doi: 10.1002/ird.1964. - DOI
-
- Ahmad H., Hayat S., Ali M., Liu T., Cheng Z.H. The combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation (Glomus versiforme) and 28-homobrassinolide spraying intervals improves growth by enhancing photosynthesis, nutrient absorption, and antioxidant system in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) under salinity. Evol. Ecol. 2018;8:5724–5740. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharma A., Kumar V., Shahzad B., Ramakrishnan M., Zheng B.S. Photosynthetic response of plants under different abiotic stresses: A review. Plant Growth Regul. 2020;39:509–531. doi: 10.1007/s00344-019-10018-x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022B02021-3-1/The research was funded by the Major Science and Technology Project and Key Research and Development of Autonomous region, Xinjiang, China
- (Title: Research and demonstration on the key technologies of soil improvement and ecological prevention and control in the desert desert belt of Southern Xinjiang)/The Central Government Guides Local Science and Technology Development Fund Projects
- CXFZ202207/Shihezi University Innovative Development Special Projectand, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

