The Biology and Genomics of Human Hair Follicles: A Focus on Androgenetic Alopecia
- PMID: 38473791
- PMCID: PMC10932098
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052542
The Biology and Genomics of Human Hair Follicles: A Focus on Androgenetic Alopecia
Abstract
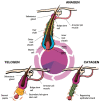
Androgenetic alopecia is a highly prevalent condition mainly affecting men. This complex trait is related to aging and genetics; however, multiple other factors, for example, lifestyle, are also involved. Despite its prevalence, the underlying biology of androgenetic alopecia remains elusive, and thus advances in its treatment have been hindered. Herein, we review the functional anatomy of hair follicles and the cell signaling events that play a role in follicle cycling. We also discuss the pathology of androgenetic alopecia and the known molecular mechanisms underlying this condition. Additionally, we describe studies comparing the transcriptional differences in hair follicles between balding and non-balding scalp regions. Given the genetic contribution, we also discuss the most significant risk variants found to be associated with androgenetic alopecia. A more comprehensive understanding of this pathology may be generated through using multi-omics approaches.
Keywords: androgenetic alopecia; genomics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors R.C.-D.D., M.G.-G., D.B.G., A.S.-R., C.G.-C., D.R.-S., A.F. and A.C.-L. were employed by the company CapilarFix® and/or Neomedics®. The remaining authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impairment of autophagy may be associated with follicular miniaturization in androgenetic alopecia by inducing premature catagen.J Dermatol. 2021 Mar;48(3):289-300. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15672. Epub 2020 Dec 1. J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33258150
-
A comparison of the culture and growth of dermal papilla cells from hair follicles from non-balding and balding (androgenetic alopecia) scalp.Br J Dermatol. 1996 Mar;134(3):437-44. Br J Dermatol. 1996. PMID: 8731666
-
Stem cell factor/c-Kit signalling in normal and androgenetic alopecia hair follicles.J Endocrinol. 2008 Apr;197(1):11-23. doi: 10.1677/JOE-07-0522. J Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18372228
-
Genetic and molecular aspects of androgenetic alopecia.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018 May-Jun;84(3):263-268. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_262_17. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018. PMID: 29595184 Review.
-
Age-related hair changes in men: mechanisms and management of alopecia and graying.Maturitas. 2015 Jan;80(1):58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Maturitas. 2015. PMID: 25466305 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal relationship between gut microbiota and androgenetic alopecia: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 27;103(52):e41106. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041106. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39969294 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Advances in Anti-hair Loss and Hair Regrowth Cosmeceuticals: Mechanistic Breakthroughs and Industrial Prospects Driven by Multidisciplinary Collaborative Innovation.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05077-3. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40790388 Review.
-
Changes and Correlation Between Hormones, Immunoglobulins, and Minerals in Blood Serum and Hair of Tianzhu White Yaks of Different Ages and Gender.Animals (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;15(5):682. doi: 10.3390/ani15050682. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075965 Free PMC article.
-
Can oral minoxidil be the game changer in androgenetic alopecia? A comprehensive review and meta-analysis comparing topical and oral minoxidil for treating androgenetic alopecia.Skin Health Dis. 2025 Apr 25;5(2):95-101. doi: 10.1093/skinhd/vzaf009. eCollection 2025 Apr. Skin Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40365252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Black phosphorus nanosheets encapsulated microneedle for multifunctional therapy for androgenic alopecia.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Feb 27;23(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03242-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40016758 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

