Dihydropashanone Isolated from Lindera erythrocarpa, a Potential Natural Product for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 38473792
- PMCID: PMC10931615
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052545
Dihydropashanone Isolated from Lindera erythrocarpa, a Potential Natural Product for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
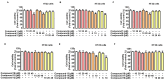
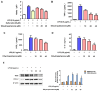
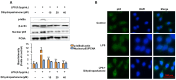
Lindera erythrocarpa, a flowering plant native to eastern Asia, has been reported to have neuroprotective activity. However, reports on the specific bioactive compounds in L. erythrocarpa are finite. The aim of this study was to investigate the anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective effects of the compounds isolated from L. erythrocarpa. Dihydropashanone, a compound isolated from L. erythrocarpa extract, was found to have protected mouse hippocampus HT22 cells from glutamate-induced cell death. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of dihydropashanone in mouse microglial BV2 and HT22 cells were explored in this study. The results reveal that dihydropashanone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response and suppresses the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB in BV2 cells. In addition, dihydropashanone reduced the buildup of reactive oxygen species in HT22 cells and induced activation of the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase (HO)-1 signaling pathway in BV2 and HT22 cells. Our results suggest that dihydropashanone reduces neuroinflammation by decreasing NF-κB activation in microglia cells and protects neurons from oxidative stress via the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Thus, our data suggest that dihydropashanone offers a broad range of applications in the treatment of neurodegenerative illnesses.
Keywords: NF-κB; Nrf2; dihydropashanone; neuroprotective effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Verma H., Gangwar P., Yadav A., Yadav B., Rao R., Kaur S., Kumar P., Dhiman M., Taglialatela G., Mantha A.K. Understanding the neuronal synapse and challenges associated with the mitochondrial dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Mitochondrion. 2023;73:19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2023.09.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

