Structural Characterization and Functional Analysis of Mevalonate Kinase from Tribolium castaneum (Red Flour Beetle)
- PMID: 38473803
- PMCID: PMC10931659
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052552
Structural Characterization and Functional Analysis of Mevalonate Kinase from Tribolium castaneum (Red Flour Beetle)
Abstract
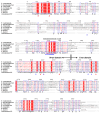
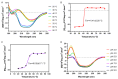
Mevalonate kinase (MevK) is an important enzyme in the mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the phosphorylation of mevalonate into phosphomevalonate and is involved in juvenile hormone biosynthesis. Herein, we present a structure model of MevK from the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (TcMevK), which adopts a compact α/β conformation that can be divided into two parts: an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain. A narrow, deep cavity accommodating the substrate and cofactor was observed at the junction between the two domains of TcMevK. Computational simulation combined with site-directed mutagenesis and biochemical analyses allowed us to define the binding mode of TcMevK to cofactors and substrates. Moreover, TcMevK showed optimal enzyme activity at pH 8.0 and an optimal temperature of 40 °C for mevalonate as the substrate. The expression profiles and RNA interference of TcMevK indicated its critical role in controlling juvenile hormone biosynthesis, as well as its participation in the production of other terpenoids in T. castaneum. These findings improve our understanding of the structural and biochemical features of insect Mevk and provide a structural basis for the design of MevK inhibitors.
Keywords: enzymatic activity; juvenile hormone biosynthesis; mevalonate pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
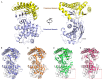



Similar articles
-
Structural insights into the substrate binding of phosphomevalonate kinase from the silkworm, Bombyx mori.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2022 Nov;150:103849. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2022.103849. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36209956
-
S6K1 acts through FOXO to regulate juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.J Insect Physiol. 2022 Jul;140:104405. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2022.104405. Epub 2022 Jun 6. J Insect Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35679992
-
The Mitochondrial Phosphatase PTPMT1 is Required for the Proper Growth Rate in the Red Flour Beetle, Tribolium castaneum.Zoolog Sci. 2022 Jun;39(3):236-241. doi: 10.2108/zs210092. Zoolog Sci. 2022. PMID: 35699926
-
A genome-wide inventory of neurohormone GPCRs in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Jan;29(1):142-65. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.10.003. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18054377 Review.
-
[When Tribolium complements the genetics of Drosophila].Med Sci (Paris). 2010 Mar;26(3):297-303. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2010263297. Med Sci (Paris). 2010. PMID: 20346280 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Energy Reserve Allocation in the Trade-Off between Migration and Reproduction in Fall Armyworm.Insects. 2024 Oct 16;15(10):809. doi: 10.3390/insects15100809. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39452385 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

