Monolacunary Wells-Dawson Polyoxometalate as a Novel Contrast Agent for Computed Tomography: A Comprehensive Study on In Vivo Toxicity and Biodistribution
- PMID: 38473818
- PMCID: PMC10932266
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052569
Monolacunary Wells-Dawson Polyoxometalate as a Novel Contrast Agent for Computed Tomography: A Comprehensive Study on In Vivo Toxicity and Biodistribution
Abstract
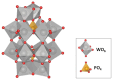
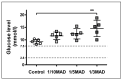
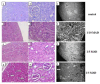
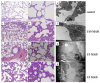
Polyoxotungstate nanoclusters have recently emerged as promising contrast agents for computed tomography (CT). In order to evaluate their clinical potential, in this study, we evaluated the in vitro CT imaging properties, potential toxic effects in vivo, and tissue distribution of monolacunary Wells-Dawson polyoxometalate, α2-K10P2W17O61.20H2O (mono-WD POM). Mono-WD POM showed superior X-ray attenuation compared to other tungsten-containing nanoclusters (its parent WD-POM and Keggin POM) and the standard iodine-based contrast agent (iohexol). The calculated X-ray attenuation linear slope for mono-WD POM was significantly higher compared to parent WD-POM, Keggin POM, and iohexol (5.97 ± 0.14 vs. 4.84 ± 0.05, 4.55 ± 0.16, and 4.30 ± 0.09, respectively). Acute oral (maximum-administered dose (MAD) = 960 mg/kg) and intravenous administration (1/10, 1/5, and 1/3 MAD) of mono-WD POM did not induce unexpected changes in rats' general habits or mortality. Results of blood gas analysis, CO-oximetry status, and the levels of electrolytes, glucose, lactate, creatinine, and BUN demonstrated a dose-dependent tendency 14 days after intravenous administration of mono-WD POM. The most significant differences compared to the control were observed for 1/3 MAD, being approximately seventy times higher than the typically used dose (0.015 mmol W/kg) of tungsten-based contrast agents. The highest tungsten deposition was found in the kidney (1/3 MAD-0.67 ± 0.12; 1/5 MAD-0.59 ± 0.07; 1/10 MAD-0.54 ± 0.05), which corresponded to detected morphological irregularities, electrolyte imbalance, and increased BUN levels.
Keywords: CO-oximetry status; X-ray attenuation; biochemical parameters; blood gas analysis; histological analysis; in vitro computed tomography imaging; in vivo toxicity; monolacunary Wells-Dawson polyoxotungstate; tissue distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Hisieh J. Computed Tomography: Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances. 3rd ed. SPIE Press; Bellingham, WA, USA: 2015.
-
- Solomon J., Marin D., Roy Choudhury K., Patel B., Samei E. Effect of Radiation Dose Reduction and Reconstruction Algorithm on Image Noise, Contrast, Resolution, and Detectability of Subtle Hypoattenuating Liver Lesions at Multidetector CT: Filtered Back Projection versus a Commercial Model-based Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm. Radiology. 2017;284:777–787. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

