Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping in Practice: A Real-World Study of the APIS Breast Cancer Subtyping Assay in a Consecutive Series of Breast Core Biopsies
- PMID: 38473863
- PMCID: PMC10931915
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052616
Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping in Practice: A Real-World Study of the APIS Breast Cancer Subtyping Assay in a Consecutive Series of Breast Core Biopsies
Abstract
The APIS Breast Cancer Subtyping Kit is an mRNA-based assessment of the seven parameters including three biomarkers routinely assessed in all the newly diagnosed breast cancers (BC), oestrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER-2 and an additional four genes that create a novel proliferation signature, MKI67, PCNA, CCNA2 and KIF23. Taken together, the data are used to produce a molecular subtype for every sample. The kit was evaluated against the current standard protocol of immunohistochemistry (IHC) and/or in situ hybridisation (ISH) in breast cancer patients. The data were presented at the weekly breast multidisciplinary team (MDT) meeting. A total of 98 consecutive cases of pre-operative breast cancer core biopsies and two core biopsies of nodal metastases yielding 100 cases were assessed. IHC and APIS results were available for 100 and 99 cases. ER was concordant in 97% cases, PR was concordant in 89% and HER-2 results were concordant with IHC/ISH in 100% of the cases. Ki-67 IHC was discordant in 3% of cases when compared with MK167 alone but discordant in 24% when compared with the four-gene proliferation signature. In conclusion, our study indicates that the APIS Breast Cancer Subtyping Kit is highly concordant when compared to the results produced for ER/PR/HER-2 by IHC and/or ISH. The assay could play a role in the routine assessment of newly diagnosed breast cancer (BC) specimens.
Keywords: APIS mRNA molecular assessment; ER; HER-2; Ki-67; PR; breast cancer; immunohistochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
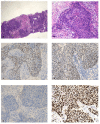
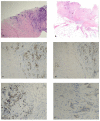
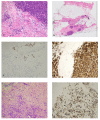
References
-
- Nielsen T.O., Parker J.S., Leung S., Voduc D., Ebbert M., Vickery T., Davies S.R., Snider J., Stijleman I.J., Reed J., et al. A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;16:5222–5232. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Palma S., Simpson R.H.W., Marchiò C., Skálová A., Ungari M., Sandison A., Whitaker S., Parry S., Reis-Filho J.S. Salivary duct carcinomas can be classified into luminal androgen receptor-positive, HER2 and basal-like phenotypes. Histopathology. 2012;61:629–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04252.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Filippou C., Themistocleous S.C., Marangos G., Panayiotou Y., Fyrilla M., Kousparou C.A., Pana Z.-D., Tsioutis C., Johnson E.O., Yiallouris A. Microbial Therapy and Breast Cancer Management: Exploring Mechanisms, Clinical Efficacy, and Integration within the One Health Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024;25:1110. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

