Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Improves Neurotoxicity in Chronic Ethanol-Induced-Dementia Mice via Suppressing AKT and NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38473876
- PMCID: PMC10931926
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052629
Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Improves Neurotoxicity in Chronic Ethanol-Induced-Dementia Mice via Suppressing AKT and NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
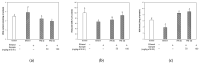
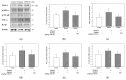
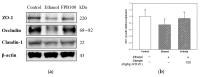
This study was investigated to examine the neuroprotective effect of fermented Protaetia brevitarsis larvae (FPB) in ethanol-induced-dementia mice. Consumption of FPB by mice resulted in improved memory dysfunction in the Y-maze, passive avoidance, and Morris water maze tests. FPB significantly decreased oxidative stress by regulating levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and reduced glutathione (GSH) in brain tissues. In addition, FPB restored cerebral mitochondrial dysfunction by modulating levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and ATP. In addition, FPB enhanced the cholinergic system via the regulation of acetylcholine (ACh) content, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, and expressions of AChE and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in brain tissues. FPB ameliorated neuronal apoptosis through modulation of the protein kinase B (AKT)/B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-2 signaling pathway. Also, FPB improved inflammation response by down-regulating the toll-like receptor (TLR)-4/nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway. Additionally, FPB ameliorated synaptic plasticity via the increase of the expressions of synaptophysin (SYP), postsynaptic density protein (PSD)-95, and growth-associated protein (GAP)-43. Treatment with FPB also reinforced the blood-brain barrier by increasing tight junctions including zonula occludens (ZO)-1, occludin, and claudin-1. In conclusion, these results show that FPB can improve cognitive impairment via AKT/NF-κB pathways in ethanol-induced-dementia mice.
Keywords: alcoholic dementia; cognitive function; edible insects; neuroinflammation; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

