HLA-G Expression/Secretion and T-Cell Cytotoxicity in Missed Abortion in Comparison to Normal Pregnancy
- PMID: 38473890
- PMCID: PMC10932117
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052643
HLA-G Expression/Secretion and T-Cell Cytotoxicity in Missed Abortion in Comparison to Normal Pregnancy
Abstract
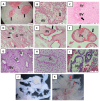
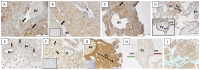
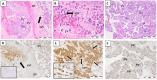
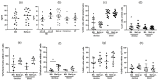
The main role of HLA-G is to protect the semi-allogeneic embryo from immune rejection by proper interaction with its cognate receptors on the maternal immune cells. Spontaneous abortion is the most common adverse pregnancy outcome, with an incidence rate between 10% and 15%, with immunologic dysregulation being thought to play a role in some of the cases. In this study, we aimed to detect the membrane and soluble HLA-G molecule at the maternal-fetal interface (MFI) and in the serum of women experiencing missed abortion (asymptomatic early pregnancy loss) in comparison to the women experiencing normal early pregnancy. In addition, the proportion of T cells and their cytotoxic profile was evaluated. We observed no difference in the spatial expression of HLA-G at the MFI and in its serum levels between the women with missed abortions and those with normal early pregnancy. In addition, comparable numbers of peripheral blood and decidual total T and γδT cells were found. In addition, as novel data we showed that missed abortion is not associated with altered extravilous invasion into uterine blood vessels and increased cytotoxicity of γδT cells. A strong signal for HLA-G on non-migrating extravilous trophoblast in the full-term normal placental bed was detected. In conclusion, HLA-G production at the MFI or in the blood of the women could not be used as a marker for normal pregnancy or missed abortions.
Keywords: HLA-G; T cells; missed abortion; γδ T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of HLA-G and KIR2DL4 receptor in chorionic villous in missed abortion.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2020;36(sup1):43-47. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2020.1816716. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 33305671
-
Maternal serum soluble HLA-G levels in missed abortions.Medicina (Kaunas). 2013;49(10):435-8. Medicina (Kaunas). 2013. PMID: 24709785
-
HLA-G isoforms, HLA-C allotype and their expressions differ between early abortus and placenta in relation to spontaneous abortions.Placenta. 2024 Apr;149:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2024.02.009. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Placenta. 2024. PMID: 38492472
-
Immunological relationship between the mother and the fetus.Int Rev Immunol. 2002 Nov-Dec;21(6):471-95. doi: 10.1080/08830180215017. Int Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12650238 Review.
-
The role of γδ-T cells during human pregnancy.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2017 Aug;78(2). doi: 10.1111/aji.12713. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28653491 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into Reproductive Immunology and Placental Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 12;25(22):12135. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212135. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596208 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygous AA Genotype of IL-17A and 14-bp Insertion Polymorphism in HLA-G 3'UTR Are Associated with Increased Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Feb 22;22(3):327. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22030327. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40238306 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

