MiR-290 Family Maintains Pluripotency and Self-Renewal by Regulating MAPK Signaling Pathway in Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 38473927
- PMCID: PMC10931995
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052681
MiR-290 Family Maintains Pluripotency and Self-Renewal by Regulating MAPK Signaling Pathway in Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
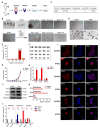
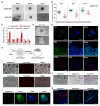
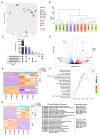
Mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) are derived from pre- and post-implantation embryos, representing the initial "naïve" and final "primed" states of pluripotency, respectively. In this study, novel reprogrammed pluripotent stem cells (rPSCs) were induced from mouse EpiSCs using a chemically defined medium containing mouse LIF, BMP4, CHIR99021, XAV939, and SB203580. The rPSCs exhibited domed clones and expressed key pluripotency genes, with both X chromosomes active in female cells. Furthermore, rPSCs differentiated into cells of all three germ layers in vivo through teratoma formation. Regarding epigenetic modifications, the DNA methylation of Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog promoter regions and the mRNA levels of Dnmt3a, Dnmt3b, and Dnmt1 were reduced in rPSCs compared with EpiSCs. However, the miR-290 family was significantly upregulated in rPSCs. After removing SB203580, an inhibitor of the p38 MAPK pathway, the cell colonies changed from domed to flat, with a significant decrease in the expression of pluripotency genes and the miR-290 family. Conversely, overexpression of pri-miR-290 reversed these changes. In addition, Map2k6 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-291b-3p, indicating that the miR-290 family maintains pluripotency and self-renewal in rPSCs by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: intermediate state; miR-290 family; naïve stem cells; p38 MAPK signaling pathway; pluripotency; primed stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Timely stimulation of early embryo promotes the acquisition of pluripotency.Cytometry A. 2022 Aug;101(8):682-691. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.24551. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Cytometry A. 2022. PMID: 35332996
-
Neural stem cells derived from epiblast stem cells display distinctive properties.Stem Cell Res. 2014 Mar;12(2):506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.12.012. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Stem Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24463498
-
Accessing naïve human pluripotency.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Jun;22(3):272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22463982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient derivation of bovine embryonic stem cells needs more than active core pluripotency factors.Mol Reprod Dev. 2012 Jul;79(7):461-77. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22051. Epub 2012 May 31. Mol Reprod Dev. 2012. PMID: 22573702
-
Stepwise pluripotency transitions in mouse stem cells.EMBO Rep. 2022 Sep 5;23(9):e55010. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255010. Epub 2022 Jul 29. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35903955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

