Anti Gram-Positive Bacteria Activity of Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Lipid and Its Precursor Phosphonium Salt
- PMID: 38474008
- PMCID: PMC10931589
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052761
Anti Gram-Positive Bacteria Activity of Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Lipid and Its Precursor Phosphonium Salt
Abstract
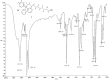
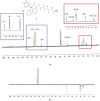
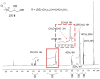
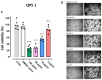
Organic ammonium and phosphonium salts exert excellent antimicrobial effects by interacting lethally with bacterial membranes. Particularly, quaternary ammonium lipids have demonstrated efficiency both as gene vectors and antibacterial agents. Here, aiming at finding new antibacterial devices belonging to both classes, we prepared a water-soluble quaternary ammonium lipid (6) and a phosphonium salt (1) by designing a synthetic path where 1 would be an intermediate to achieve 6. All synthesized compounds were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Additionally, potentiometric titrations of NH3+ groups 1 and 6 were performed to further confirm their structure by determining their experimental molecular weight. The antibacterial activities of 1 and 6 were assessed first against a selection of multi-drug-resistant clinical isolates of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative species, observing remarkable antibacterial activity of both compounds against Gram-positive isolates of Enterococcus and Staphylococcus genus. Further investigations on a wider variety of strains of these species confirmed the remarkable antibacterial effects of 1 and 6 (MICs = 4-16 and 4-64 µg/mL, respectively), while 24 h-time-killing experiments carried out with 1 on different S. aureus isolates evidenced a bacteriostatic behavior. Moreover, both compounds 1 and 6, at the lower MIC concentration, did not show significant cytotoxic effects when exposed to HepG2 human hepatic cell lines, paving the way for their potential clinical application.
Keywords: Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; MICs determination; cytotoxicity studies; membrane permeabilization; multi-drug-resistant bacteria; phosphonium salt (1); quaternary ammonium lipid (6); time-killing experiments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synthesized Bis-Triphenyl Phosphonium-Based Nano Vesicles Have Potent and Selective Antibacterial Effects on Several Clinically Relevant Superbugs.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;14(16):1351. doi: 10.3390/nano14161351. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195389 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the structure of chitosan quaternary phosphonium salt and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt on the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jul 1;242(Pt 2):124877. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124877. Epub 2023 May 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37182629
-
Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal Activity of a Synthetic Random Copolymer Based on 2-Methoxy-6-(4-Vinylbenzyloxy)-Benzylammonium Hydrochloride.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 9;22(9):5021. doi: 10.3390/ijms22095021. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34065133 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial potential of quaternary phosphonium salt compounds: a review.Future Med Chem. 2023 Nov;15(22):2113-2141. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2023-0188. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Future Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37929337 Review.
-
Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Feb 6;16(2):3626-55. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023626. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25667977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strongly ROS-Correlated, Time-Dependent, and Selective Antiproliferative Effects of Synthesized Nano Vesicles on BRAF Mutant Melanoma Cells and Their Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10071. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810071. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337557 Free PMC article.
-
The Remarkable and Selective In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Synthesized Bola-Amphiphilic Nanovesicles on Etoposide-Sensitive and -Resistant Neuroblastoma Cells.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Sep 16;14(18):1505. doi: 10.3390/nano14181505. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330662 Free PMC article.
-
TPP-Based Nanovesicles Kill MDR Neuroblastoma Cells and Induce Moderate ROS Increase, While Exerting Low Toxicity Towards Primary Cell Cultures: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):4991. doi: 10.3390/ijms26114991. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507803 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Ocular Drug Delivery: The Impact of Permeation Enhancers.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 31;17(4):447. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040447. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesized Bis-Triphenyl Phosphonium-Based Nano Vesicles Have Potent and Selective Antibacterial Effects on Several Clinically Relevant Superbugs.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;14(16):1351. doi: 10.3390/nano14161351. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- My Personal Trailer. [(accessed on 15 April 2021)]. Available online: https://www.my-personaltrainer.it/farmaci/citrosil.html.
-
- Lei Y., Zhou S., Dong C., Zhang A., Lin Y. PDMS Tri-Block Copolymers Bearing Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Epidermal Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Surface Adsorption and Non-Skin-Penetration. React. Funct. Polym. 2018;124:20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.01.007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

