Advances in HIV Gene Therapy
- PMID: 38474018
- PMCID: PMC10931721
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052771
Advances in HIV Gene Therapy
Abstract
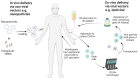
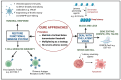
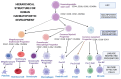
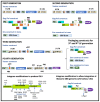
Early gene therapy studies held great promise for the cure of heritable diseases, but the occurrence of various genotoxic events led to a pause in clinical trials and a more guarded approach to progress. Recent advances in genetic engineering technologies have reignited interest, leading to the approval of the first gene therapy product targeting genetic mutations in 2017. Gene therapy (GT) can be delivered either in vivo or ex vivo. An ex vivo approach to gene therapy is advantageous, as it allows for the characterization of the gene-modified cells and the selection of desired properties before patient administration. Autologous cells can also be used during this process which eliminates the possibility of immune rejection. This review highlights the various stages of ex vivo gene therapy, current research developments that have increased the efficiency and safety of this process, and a comprehensive summary of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) gene therapy studies, the majority of which have employed the ex vivo approach.
Keywords: HIV; ex vivo; gene therapy; stem cells; vector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Human Genome Research Institute The Human Genome Project Results. The Human Genome Project 2003. [(accessed on 5 July 2022)]; Available online: https://www.genome.gov/human-genome-project/results.
-
- Berdeja J.G., Madduri D., Usmani S.Z., Jakubowiak A., Agha M., Cohen A.D., Stewart A.K., Hari P., Htut M., Lesokhin A., et al. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CARTITUDE-1): A phase 1b/2 open-label study. Lancet. 2021;398:314–324. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00933-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abramson J.S., Palomba M.L., Gordon L.I., Lunning M.A., Wang M., Arnason J., Mehta A., Purev E., Maloney D.G., Andreadis C., et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396:839–852. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31366-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

