Genetic Loci of Plant Pathogenic Dickeya solani IPO 2222 Expressed in Contact with Weed-Host Bittersweet Nightshade (Solanum dulcamara L.) Plants
- PMID: 38474041
- PMCID: PMC10931765
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052794
Genetic Loci of Plant Pathogenic Dickeya solani IPO 2222 Expressed in Contact with Weed-Host Bittersweet Nightshade (Solanum dulcamara L.) Plants
Abstract
Dickeya solani, belonging to the Soft Rot Pectobacteriaceae, are aggressive necrotrophs, exhibiting both a wide geographic distribution and a wide host range that includes many angiosperm orders, both dicot and monocot plants, cultivated under all climatic conditions. Little is known about the infection strategies D. solani employs to infect hosts other than potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Our earlier study identified D. solani Tn5 mutants induced exclusively by the presence of the weed host S. dulcamara. The current study assessed the identity and virulence contribution of the selected genes mutated by the Tn5 insertions and induced by the presence of S. dulcamara. These genes encode proteins with functions linked to polyketide antibiotics and polysaccharide synthesis, membrane transport, stress response, and sugar and amino acid metabolism. Eight of these genes, encoding UvrY (GacA), tRNA guanosine transglycosylase Tgt, LPS-related WbeA, capsular biosynthesis protein VpsM, DltB alanine export protein, glycosyltransferase, putative transcription regulator YheO/PAS domain-containing protein, and a hypothetical protein, were required for virulence on S. dulcamara plants. The implications of D. solani interaction with a weed host, S. dulcamara, are discussed.
Keywords: Erwinia chrysanthemi; Tn5; alternative plant host; colonization; qRT-PCR; random transposon mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
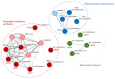
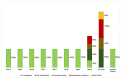
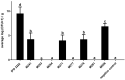
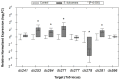
Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Dickeya solani Transcriptional Units Up-Regulated in Response to Plant Tissues From a Crop-Host Solanum tuberosum and a Weed-Host Solanum dulcamara.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 2;11:580330. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.580330. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32983224 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Colonization and Expression of Disease Symptoms on Bittersweet Nightshade (Solanum dulcamara) Infected with a GFP-Tagged Dickeya solani IPO2222 (IPO2254).Plant Dis. 2018 Mar;102(3):619-627. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-17-1147-RE. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Plant Dis. 2018. PMID: 30673477
-
High-Quality Complete Genome Resource of Plant-Pathogenic Bacterium Dickeya solani IPO 2019, Isolated from Hyacinthus orientalis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021 Sep;34(9):1088-1092. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-21-0050-A. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021. PMID: 33861631
-
Looking for Resistance to Soft Rot Disease of Potatoes Facing Environmental Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 28;25(7):3757. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073757. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spirosolane-containing Solanum species and induction of congenital craniofacial malformations.Toxicon. 1990;28(8):873-84. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90017-2. Toxicon. 1990. PMID: 2080514 Review.
References
-
- Buonaurio R. Infection and plant defense responses during plant-bacterial interaction. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008:169–197.
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

