Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Inhibits Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity in Phorbol 12-Myristate-13-Acetate-Induced Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 38474055
- PMCID: PMC10932471
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052806
Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Inhibits Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity in Phorbol 12-Myristate-13-Acetate-Induced Endothelial Cells
Abstract
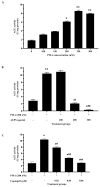
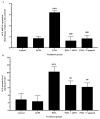
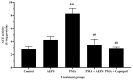
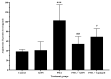
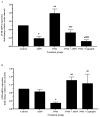
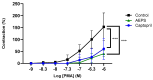
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Piper sarmentosum Roxb., an herb known for its antihypertensive effect, lacks a comprehensive understanding of the mechanism underlying its antihypertensive action. This study aimed to elucidate the antihypertensive mechanism of aqueous extract of P. sarmentosum leaves (AEPS) via its modulation of the ACE pathway in phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). HUVECs were divided into five groups: control, treatment with 200 µg/mL AEPS, induction 200 nM PMA, concomitant treatment with 200 nM PMA and 200 µg/mL AEPS, and treatment with 200 nM PMA and 0.06 μM captopril. Subsequently, ACE mRNA expression, protein level and activity, angiotensin II (Ang II) levels, and angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) mRNA expression in HUVECs were determined. AEPS successfully inhibited ACE mRNA expression, protein and activity, and angiotensin II levels in PMA-induced HUVECs. Additionally, AT1R expression was downregulated, whereas AT2R expression was upregulated. In conclusion, AEPS reduces the levels of ACE mRNA, protein and activity, Ang II, and AT1R expression in PMA-induced HUVECs. Thus, AEPS has the potential to be developed as an ACE inhibitor in the future.
Keywords: Piper sarmentosum; angiotensin converting enzyme; human umbilical vein endothelial cells; hypertension; phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. GBD-NHLBI-JACC Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Writing Group. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S., Joseph P., Rangarajan S., Islam S., Mente A., Hystad P., Brauer M., Kutty V.R., Gupta R., Wielgosz A., et al. Modifiable risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in 155,722 individuals from 21 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:795–808. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32008-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Đambić V., Pojatić Đ., Stažić A., Kibel A. Significance of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Clinical Conditions. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

