Clinical Insights into MicroRNAs in Depression: Bridging Molecular Discoveries and Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 38474112
- PMCID: PMC10931847
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052866
Clinical Insights into MicroRNAs in Depression: Bridging Molecular Discoveries and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
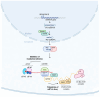
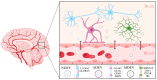
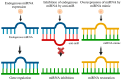
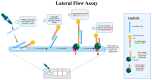
Depression is a major contributor to the overall global burden of disease. The discovery of biomarkers for diagnosis or prediction of treatment responses and as therapeutic agents is a current priority. Previous studies have demonstrated the importance of short RNA molecules in the etiology of depression. The most extensively researched of these are microRNAs, a major component of cellular gene regulation and function. MicroRNAs function in a temporal and tissue-specific manner to regulate and modify the post-transcriptional expression of target mRNAs. They can also be shuttled as cargo of extracellular vesicles between the brain and the blood, thus informing about relevant mechanisms in the CNS through the periphery. In fact, studies have already shown that microRNAs identified peripherally are dysregulated in the pathological phenotypes seen in depression. Our article aims to review the existing evidence on microRNA dysregulation in depression and to summarize and evaluate the growing body of evidence for the use of microRNAs as a target for diagnostics and RNA-based therapies.
Keywords: antidepressant; biomarker; depression; extracellular vesicles; major depressive disorder; miRNA therapeutics; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miRNAs in prostate cancer: Intercellular and extracellular communications.Int J Urol. 2022 Dec;29(12):1429-1438. doi: 10.1111/iju.15043. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Int J Urol. 2022. PMID: 36122303 Review.
-
The miRNome of Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 20;22(21):11312. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111312. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct transcriptional regulation by nuclear microRNAs.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;54:304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24680896 Review.
-
miRNA regulation of social and anxiety-related behaviour.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(21):4347-4364. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03542-7. Epub 2020 May 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32409861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: aberrant microRNA expression in Alzheimer's disease brains.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114(3):269-75. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10r11fm. Epub 2010 Oct 9. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20953120 Review.
Cited by
-
BDNF Modulation by microRNAs: An Update on the Experimental Evidence.Cells. 2024 May 20;13(10):880. doi: 10.3390/cells13100880. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38786102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: A Novel Approach for Monitoring Treatment Response in Major Depressive Disorder?Noncoding RNA. 2025 Mar 3;11(2):21. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020021. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA signatures in neuroplasticity, neuroinflammation and neurotransmission in association with depression.J Physiol Biochem. 2025 Feb;81(1):85-97. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01065-4. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39695016 Review.
-
Exosomes in Regulating miRNAs for Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7576-7596. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04733-8. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39918711 Review.
-
Advances and challenges in the use of liquid biopsy in gynaecological oncology.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 15;10(20):e39148. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39148. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39492906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation . Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation; Seattle, WA, USA: 2021.
-
- James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nihalani N., Simionescu M., Dunlop B.W. Depression. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2010. Depression: Phenomenology, Epidemiology, and Pathophysiology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

