Eicosapentaenoic Acid Modulates Transient Receptor Potential V1 Expression in Specific Brain Areas in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Pain Model
- PMID: 38474148
- PMCID: PMC10932372
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052901
Eicosapentaenoic Acid Modulates Transient Receptor Potential V1 Expression in Specific Brain Areas in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Pain Model
Abstract
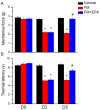
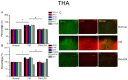
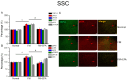
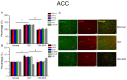
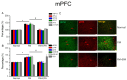
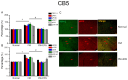
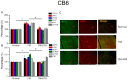
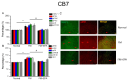
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience accompanied by tissue injury. Often, an individual's experience can be influenced by different physiological, psychological, and social factors. Fibromyalgia, one of the most difficult-to-treat types of pain, is characterized by general muscle pain accompanied by obesity, fatigue, sleep, and memory and psychological concerns. Fibromyalgia increases nociceptive sensations via central sensitization in the brain and spinal cord level. We used intermittent cold stress to create a mouse fibromyalgia pain model via a von Frey test (day 0: 3.69 ± 0.14 g; day 5: 2.13 ± 0.12 g). Mechanical pain could be reversed by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) administration (day 0: 3.72 ± 0.14 g; day 5: 3.69 ± 0.13 g). A similar trend could also be observed for thermal hyperalgesia. The levels of elements in the transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) signaling pathway were increased in the ascending pain pathway, including the thalamus, medial prefrontal cortex, somatosensory cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and cerebellum. EPA intake significantly attenuated this overexpression. A novel chemogenetics method was used to inhibit SSC and ACC activities, which presented an analgesic effect through the TRPV1 downstream pathway. The present results provide insights into the role of the TRPV1 signaling pathway for fibromyalgia and its potential as a clinical target.
Keywords: TRPV1; eicosapentaenoic acid; fibromyalgia; mPFC; thalamus.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other relationships that might lead to conflicts of interest for all authors.
Figures
References
-
- Masood R., Mandalia K., Moverman M.A., Puzzitiello R.N., Pagani N.R., Menendez M.E., Salzler M.J. Patients with Functional Somatic Syndromes-Fibromyalgia, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Chronic Headaches, and Chronic Low Back Pain-Have Lower Outcomes and Higher Opioid Usage and Cost After Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. Arthroscopy. 2023;39:1529–1538. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2022.12.028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

