A Review on the Role and Function of Cinnabarinic Acid, a "Forgotten" Metabolite of the Kynurenine Pathway
- PMID: 38474418
- PMCID: PMC10930587
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13050453
A Review on the Role and Function of Cinnabarinic Acid, a "Forgotten" Metabolite of the Kynurenine Pathway
Abstract
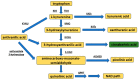
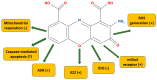
In the human body, the majority of tryptophan is metabolized through the kynurenine pathway. This consists of several metabolites collectively called the kynurenines and includes, among others, kynurenic acid, L-kynurenine, or quinolinic acid. The wealth of metabolites, as well as the associated molecular targets and biological pathways, bring about a situation wherein even a slight imbalance in the kynurenine levels, both in the periphery and central nervous system, have broad consequences regarding general health. Cinnabarinic acid (CA) is the least known trace kynurenine, and its physiological and pathological roles are not widely understood. Some studies, however, indicate that it might be neuroprotective. Information on its hepatoprotective properties have also emerged, although these are pioneering studies and need to be replicated. Therefore, in this review, I aim to present and critically discuss the current knowledge on CA and its role in physiological and pathological settings to guide future studies.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; cinnabarinic acid; kynurenine pathway; metabotropic glutamate receptor; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An expanding range of targets for kynurenine metabolites of tryptophan.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Feb;34(2):136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23123095 Review.
-
Cinnabarinic acid and xanthurenic acid: Two kynurenine metabolites that interact with metabotropic glutamate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jan;112(Pt B):365-372. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.06.020. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27342123 Review.
-
A review of chromatographic methods for bioactive tryptophan metabolites, kynurenine, kynurenic acid, quinolinic acid, and others, in biological fluids.Biomed Chromatogr. 2022 May;36(5):e5308. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5308. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Biomed Chromatogr. 2022. PMID: 34978092 Review.
-
Unstability of cinnabarinic acid, an endogenous metabolite of tryptophan, under situations mimicking physiological conditions.Biochimie. 2022 Aug;199:150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2022.04.009. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Biochimie. 2022. PMID: 35469990
-
Effects of immune activation on quinolinic acid and neuroactive kynurenines in the mouse.Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(1):25-39. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90467-g. Neuroscience. 1992. PMID: 1465184
Cited by
-
Diverse Physiological Roles of Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites: Updated Implications for Health and Disease.Metabolites. 2025 Mar 20;15(3):210. doi: 10.3390/metabo15030210. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40137174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tryptophan As a New Member of RNA-Induced Silencing Complexes Prevents Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(31):e2307937. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307937. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39031551 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining Roles: A Paradigm Shift in Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism for Innovative Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12767. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312767. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684480 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

